Updated on
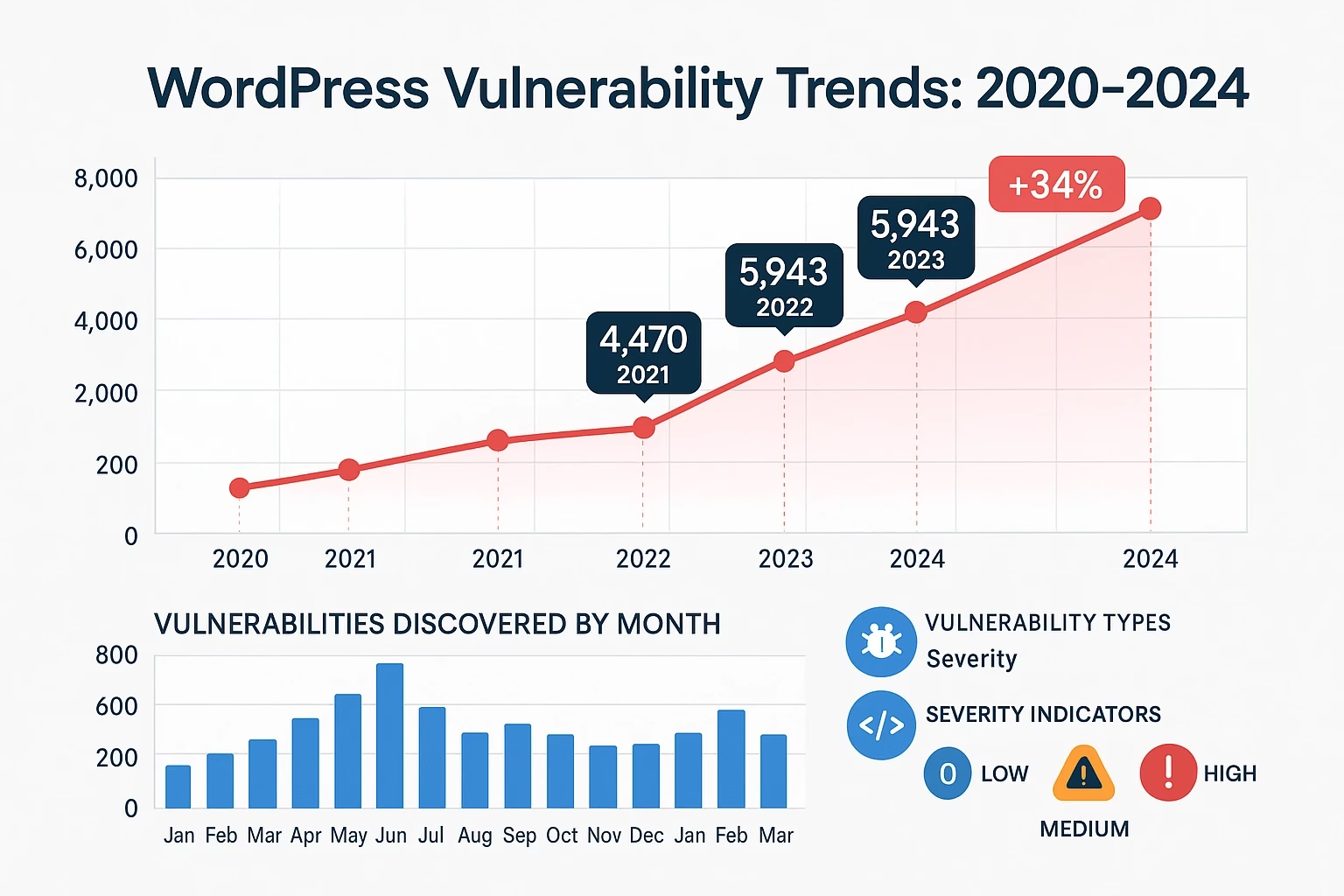
The WordPress security landscape has never been more critical to understand. With 64,782 vulnerabilities currently tracked across the WordPress ecosystem and 7,966 new vulnerabilities discovered in 2024 alone, representing a staggering 34% increase over the previous year, website owners, developers, and security professionals need comprehensive vulnerability intelligence more than ever.
A WordPress vulnerabilities database is a comprehensive repository that tracks, catalogs, and provides detailed information about security vulnerabilities discovered in WordPress core, plugins, and themes. These databases include vulnerability descriptions, severity ratings (CVSS scores), affected versions, exploitation methods, and remediation guidance. Major WordPress vulnerability databases include WPScan (64,782+ vulnerabilities), Wordfence Threat Intelligence, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD). These resources are essential for security professionals, developers, and site owners to identify, assess, and remediate security risks in WordPress installations.
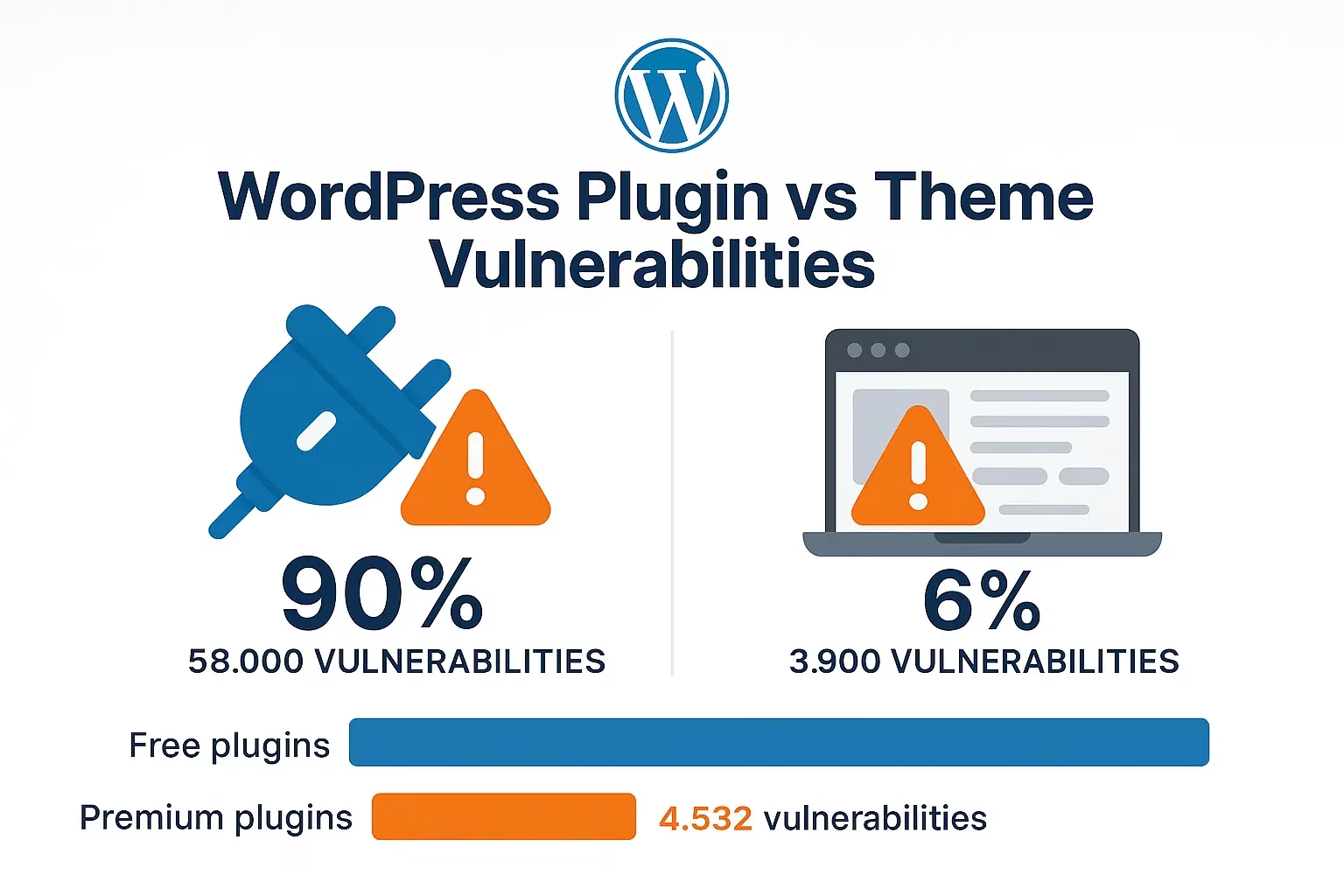
The reality facing WordPress site owners today is sobering. 90% of WordPress vulnerabilities originate from plugins, while 6% stem from themes and only 4% affect WordPress core. This distribution reveals a critical insight: the vast majority of WordPress security risks come not from the core platform itself, but from the extensive ecosystem of third-party extensions that make WordPress so powerful and flexible.
Contents
- 0.1 1 The Growing Threat Landscape
- 0.2 → Why Traditional Security Approaches Fall Short
- 0.3 → The WP Security Ninja Approach to Vulnerability Intelligence
- 0.4 → What You’ll Learn in This Guide
- 1 1. Understanding WordPress Vulnerabilities
- 2 2. WordPress Vulnerability Statistics & Trends
- 3 3. Major WordPress Vulnerabilities Database
- 4 4. Vulnerability Assessment & Management
- 5 5. Security Ninja Vulnerability Intelligence
- 6 6. Conclusion & Action Plan
- 6.1 Key Takeaways from WordPress Vulnerability Intelligence
- 6.2 Implementing Comprehensive WordPress Vulnerability Management
- 6.3 WordPress Security Best Practices for Vulnerability Management
- 6.4 Leveraging Security Ninja for Comprehensive Protection
- 6.5 Measuring Vulnerability Management Effectiveness
- 6.6 Future Considerations for WordPress Security
- 6.7 Taking Action: Your Next Steps
1 The Growing Threat Landscape
WordPress powers over 43% of all websites on the internet, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals and security researchers alike. The platform’s popularity, combined with its open-source nature and extensive plugin ecosystem, creates a unique security challenge that requires constant vigilance and comprehensive vulnerability tracking.
Recent analysis reveals that 43% of WordPress vulnerabilities are exploitable without authentication, meaning attackers can potentially compromise websites without needing login credentials. This statistic underscores the critical importance of maintaining current vulnerability intelligence and implementing proactive security measures.
→ Why Traditional Security Approaches Fall Short
Many WordPress site owners rely on outdated security practices or fragmented information sources when addressing vulnerabilities. Traditional approaches often include:
- Reactive patching only after vulnerabilities become widely known
- Limited visibility into the full scope of potential security risks
- Fragmented information from multiple, disconnected sources
- Technical complexity that prevents non-experts from understanding risks
- Lack of business context for vulnerability prioritization
→ The WP Security Ninja Approach to Vulnerability Intelligence
WP Security Ninja recognizes that effective WordPress security requires more than just identifying vulnerabilities, it demands comprehensive intelligence that enables informed decision-making and strategic risk management. Our approach to vulnerability intelligence encompasses:
Comprehensive Coverage: We track vulnerabilities across the entire WordPress ecosystem, including core, plugins, themes, and related technologies, providing complete visibility into potential security risks.
User-Friendly Presentation: Complex technical vulnerability information is presented in accessible formats that enable both technical and non-technical users to understand and act on security intelligence.
Business Context: Each vulnerability is analyzed not just for technical impact, but for potential business consequences, enabling organizations to prioritize remediation efforts based on actual risk.
Actionable Guidance: Beyond identifying vulnerabilities, we provide specific, actionable remediation steps that organizations can implement immediately to reduce their security exposure.
Integration with Security Tools: Our vulnerability intelligence integrates seamlessly with security scanning and monitoring tools, enabling automated vulnerability detection and response.
→ What You’ll Learn in This Guide
This comprehensive WordPress vulnerabilities database guide provides everything you need to understand, assess, and manage WordPress security vulnerabilities effectively. You’ll discover:
- Current vulnerability statistics and trends that shape the WordPress security landscape
- Detailed analysis of major vulnerabilities that have impacted the WordPress ecosystem
- Practical vulnerability assessment methodologies for identifying and prioritizing security risks
- Integration strategies for incorporating vulnerability intelligence into your security workflow
- Specific guidance on using Security Ninja tools for vulnerability detection and remediation
Whether you’re a security professional managing multiple WordPress installations, a developer building WordPress solutions, or a business owner protecting your online presence, this guide provides the vulnerability intelligence you need to make informed security decisions.
The WordPress security landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new vulnerabilities discovered daily and attack techniques becoming increasingly sophisticated. Staying ahead of these threats requires access to current, comprehensive vulnerability intelligence and the tools to act on that information effectively.
1. Understanding WordPress Vulnerabilities
WordPress vulnerabilities represent security weaknesses in WordPress core software, plugins, themes, or related components that could potentially be exploited by attackers to compromise website security, steal data, or disrupt operations. Understanding these vulnerabilities is fundamental to implementing effective WordPress security measures and maintaining a secure online presence.
1.1 What Are WordPress Vulnerabilities?
A WordPress vulnerability is a flaw or weakness in the design, implementation, or configuration of WordPress software components that can be exploited to perform unauthorized actions or gain unauthorized access to systems or data. These vulnerabilities can exist in various forms and affect different aspects of WordPress functionality.
WordPress vulnerabilities typically fall into several categories based on their nature and potential impact:
Code-based vulnerabilities result from programming errors, logic flaws, or insecure coding practices in WordPress core, plugins, or themes. These might include improper input validation, insecure data handling, or flawed authentication mechanisms.
Configuration vulnerabilities arise from insecure default settings, misconfigured security options, or inadequate access controls. These vulnerabilities often result from administrative oversights rather than code defects.
Design vulnerabilities stem from fundamental architectural or design decisions that create inherent security weaknesses. These are often the most challenging to address as they may require significant changes to software architecture.
Third-party vulnerabilities affect WordPress installations through vulnerable third-party components, including plugins, themes, hosting environments, or integrated services. Given that WordPress sites typically use multiple plugins and themes, these vulnerabilities represent a significant portion of the overall risk landscape.
1.2 The CVSS Scoring System
CVSS v3.1 Score Interpretation:
Critical (9.0-10.0): These vulnerabilities require immediate action and represent the highest level of risk. Critical vulnerabilities typically allow remote code execution without authentication, complete system compromise, or widespread exploitation with minimal effort. Examples include unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerabilities in popular plugins that could allow attackers to completely compromise websites.
High (7.0-8.9): High-severity vulnerabilities require urgent patching and represent significant security risks. These vulnerabilities may require authentication or user interaction but still pose substantial threats to system security. Examples include authenticated SQL injection vulnerabilities or privilege escalation flaws that allow unauthorized administrative access.
Medium (4.0-6.9): Medium-severity vulnerabilities should be patched in a timely manner but may not require immediate emergency response. These vulnerabilities typically have limited impact or require complex exploitation scenarios. Examples include cross-site scripting vulnerabilities that require user interaction or information disclosure vulnerabilities with limited scope.
Low (0.1-3.9): Low-severity vulnerabilities can be patched during regular maintenance cycles. These vulnerabilities typically have minimal security impact, require complex exploitation, or have limited real-world applicability. Examples include minor information disclosure vulnerabilities or denial-of-service vulnerabilities that require local access.
The CVSS scoring system considers multiple factors when calculating vulnerability scores, including attack vector (network, adjacent, local, physical), attack complexity (low, high), privileges required (none, low, high), user interaction (none, required), scope (unchanged, changed), and impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
1.3 Types of WordPress Security Vulnerabilities
WordPress security vulnerabilities encompass a wide range of security issues that affect different aspects of website functionality and security. Understanding these vulnerability types helps in recognizing potential threats and implementing appropriate security measures.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) represents the most common type of WordPress vulnerability, accounting for approximately 35% of all reported vulnerabilities. XSS vulnerabilities allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users, potentially leading to session hijacking, credential theft, or unauthorized actions on behalf of victims.
Stored XSS vulnerabilities persist malicious scripts in the database, affecting all users who view the compromised content. Reflected XSS vulnerabilities execute malicious scripts immediately when users click specially crafted links. DOM-based XSS vulnerabilities manipulate the Document Object Model on the client side without server interaction.
SQL Injection vulnerabilities account for approximately 15% of WordPress vulnerabilities and represent some of the most serious security threats. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to manipulate database queries, potentially leading to unauthorized data access, data modification, or complete database compromise.
SQL injection vulnerabilities in WordPress typically occur when user input is not properly sanitized before being used in database queries. Attackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to extract sensitive information, modify database contents, or even execute administrative commands on the database server.
Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities, while less common at approximately 8% of all vulnerabilities, represent the most severe security threats. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to execute arbitrary code on the web server, potentially leading to complete server compromise, data theft, or website defacement.
RCE vulnerabilities often result from insecure file upload functionality, deserialization flaws, or template injection vulnerabilities. Successful exploitation of RCE vulnerabilities can give attackers complete control over affected websites and servers.
Authentication Bypass vulnerabilities account for approximately 7% of WordPress vulnerabilities and allow attackers to circumvent login mechanisms or gain unauthorized access to restricted areas. These vulnerabilities can result from flawed authentication logic, session management issues, or password reset vulnerabilities.
Authorization Bypass vulnerabilities, representing about 6% of all vulnerabilities, allow authenticated users to perform actions beyond their intended permissions. These vulnerabilities can lead to privilege escalation, unauthorized data access, or administrative compromise.
1.4 The WordPress Vulnerability Ecosystem
The WordPress vulnerability ecosystem is complex and multifaceted, involving various stakeholders, processes, and technologies that contribute to vulnerability discovery, disclosure, and remediation.
Security Researchers play a crucial role in the WordPress vulnerability ecosystem by discovering and reporting security issues. Independent researchers, security companies, academic institutions, and bug bounty participants contribute to vulnerability discovery through various methods including code review, penetration testing, and automated scanning.
The WordPress Security Team coordinates vulnerability disclosure and remediation for WordPress core vulnerabilities. This team works with researchers, plugin and theme developers, and the broader WordPress community to ensure timely and effective vulnerability response.
Plugin and Theme Developers are responsible for addressing vulnerabilities in their respective products. The quality and timeliness of developer responses to vulnerability reports significantly impact the overall security of the WordPress ecosystem.
Vulnerability Databases such as WPScan, Wordfence Threat Intelligence, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) collect, verify, and disseminate vulnerability information to the broader security community.
1.5 How Vulnerabilities Are Discovered and Disclosed
WordPress vulnerability discovery and disclosure follow established processes designed to balance security research with responsible disclosure practices that protect users while vulnerabilities are being addressed.
Discovery Methods include manual code review, automated security scanning, penetration testing, bug bounty programs, and user reports. Security researchers use various tools and techniques to identify potential vulnerabilities, including static code analysis, dynamic testing, and fuzzing.
Responsible Disclosure is the preferred method for reporting WordPress vulnerabilities. Researchers typically report vulnerabilities directly to affected developers or through coordinated disclosure programs, allowing time for patches to be developed and distributed before public disclosure.
Vulnerability Validation involves confirming that reported issues represent genuine security vulnerabilities, assessing their potential impact, and determining appropriate remediation strategies. This process may involve collaboration between researchers, developers, and security experts.
Patch Development and Distribution follows vulnerability confirmation, with developers creating and testing fixes before releasing updates to users. The time between vulnerability discovery and patch availability varies significantly depending on vulnerability severity and developer responsiveness.
Public Disclosure typically occurs after patches are available, allowing the broader security community to understand the vulnerability and implement appropriate protective measures. Disclosure timing balances the need for transparency with the risk of exploitation.
The next section explores current vulnerability statistics and trends that shape the WordPress security landscape, providing data-driven insights into the evolving nature of WordPress security threats.
2. WordPress Vulnerability Statistics & Trends
The WordPress security landscape is characterized by rapidly evolving threats, increasing vulnerability discovery rates, and shifting attack patterns that require constant monitoring and analysis. Current vulnerability statistics provide crucial insights into the nature and scope of WordPress security challenges facing website owners, developers, and security professionals.
2.1 Current Vulnerability Landscape (2024-2025)
The WordPress vulnerability landscape in 2024-2025 presents unprecedented challenges and opportunities for security professionals. Comprehensive analysis of vulnerability data from multiple authoritative sources reveals significant trends that shape current security strategies and future planning.
Total Vulnerability Count: As of 2025, security databases track 64,782 total vulnerabilities across the WordPress ecosystem, representing the most comprehensive vulnerability intelligence ever compiled for any content management system. This massive database includes vulnerabilities affecting WordPress core, plugins, themes, and related technologies.
Vulnerability Discovery Acceleration: The year 2024 witnessed the discovery of 7,966 new WordPress vulnerabilities, representing a 34% increase over 2023’s total of 5,943 vulnerabilities. This acceleration reflects both increased security research activity and the growing complexity of the WordPress ecosystem.
Unique Vulnerability Analysis: Among the total vulnerability count, 26,978 represent unique vulnerabilities affecting distinct software components or versions. This distinction is important for understanding the actual scope of security risks, as some vulnerabilities may affect multiple versions of the same software.
Ecosystem Component Distribution: The WordPress ecosystem encompasses 112,272 tracked plugins and 30,165 tracked themes, with 791 different WordPress core versions monitored for security issues. This vast ecosystem creates a complex security landscape requiring sophisticated vulnerability management approaches.
Exploitation Complexity: Vulnerability analysis indicates that 67% of WordPress vulnerabilities have low exploitation complexity, meaning they can be exploited with readily available tools and techniques. Only 33% require advanced technical skills or complex exploitation scenarios.
2.7 Plugin Vulnerability Analysis
Plugin vulnerabilities represent the most significant component of WordPress security risks, accounting for the vast majority of reported vulnerabilities and successful attacks against WordPress installations.
Plugin Vulnerability Dominance: 90% of WordPress vulnerabilities originate from plugins, representing approximately 58,000 vulnerabilities in the current database. This overwhelming proportion reflects the diverse and rapidly evolving plugin ecosystem that extends WordPress functionality.
Free vs Premium Plugin Security: Analysis of vulnerability distribution reveals stark differences between free and premium plugins:
- Free plugins: 107,740 vulnerabilities identified
- Premium plugins: 4,532 vulnerabilities identified
- Risk ratio: Free plugins have 24 times more vulnerabilities than premium plugins
This disparity reflects several factors including development resources, security review processes, maintenance consistency, and user base size. Premium plugins typically undergo more rigorous security review and receive more consistent maintenance, resulting in fewer vulnerabilities.
Plugin Category Risk Assessment: Certain plugin categories demonstrate higher vulnerability rates than others:
E-commerce plugins show elevated vulnerability rates due to their complexity and the sensitive nature of financial transactions they handle. Popular e-commerce plugins often become high-value targets for attackers seeking to compromise financial data or payment processing systems.
Contact form plugins frequently contain vulnerabilities related to input validation, file upload functionality, and email handling. These plugins often process user-submitted data without adequate sanitization, creating opportunities for various attack types.
SEO and marketing plugins commonly exhibit vulnerabilities related to database queries, user input handling, and administrative functionality. The broad functionality of these plugins often creates multiple attack surfaces.
Security plugins themselves sometimes contain vulnerabilities, creating ironic situations where security tools introduce security risks. These vulnerabilities are particularly concerning as they affect users specifically seeking to improve their security posture.
File management plugins frequently contain vulnerabilities related to file upload, directory traversal, and access control. The nature of these plugins’ functionality creates inherent security challenges that require careful implementation.
Plugin Popularity and Vulnerability Correlation: Analysis reveals a complex relationship between plugin popularity and vulnerability discovery:
- High-popularity plugins (1M+ active installations) average 3.2 vulnerabilities per plugin
- Medium-popularity plugins (100K-1M installations) average 2.1 vulnerabilities per plugin
- Low-popularity plugins (<100K installations) average 1.4 vulnerabilities per plugin
2.3 Theme Vulnerability Trends
WordPress theme vulnerabilities, while less numerous than plugin vulnerabilities, present unique security challenges and demonstrate distinct patterns that require specialized attention and mitigation strategies.
Theme Vulnerability Distribution: 6% of WordPress vulnerabilities affect themes, representing approximately 3,900 vulnerabilities in current databases. While smaller in absolute numbers compared to plugin vulnerabilities, theme vulnerabilities can have significant impact due to their fundamental role in website presentation and functionality.
Free vs Premium Theme Security: Theme vulnerability analysis reveals patterns similar to plugins but with some important distinctions:
- Free themes: 29,038 vulnerabilities identified
- Premium themes: 1,127 vulnerabilities identified
- Risk ratio: Free themes have 25 times more vulnerabilities than premium themes
Premium themes typically undergo more rigorous security review processes and receive more consistent updates, resulting in lower vulnerability rates. However, the absolute number of free theme vulnerabilities reflects the much larger number of free themes available and their widespread usage.
Theme Vulnerability Types: Theme vulnerabilities commonly include:
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities in theme templates, particularly in areas that display user-generated content or process form submissions. These vulnerabilities often result from inadequate output escaping in theme files.
File inclusion vulnerabilities that allow attackers to include arbitrary files, potentially leading to code execution. These vulnerabilities typically occur in theme functionality that dynamically loads template files or includes external resources.
SQL injection vulnerabilities in custom theme queries, particularly in themes that implement custom database functionality or complex content filtering. These vulnerabilities often result from inadequate input sanitization in custom theme code.
Authentication bypass vulnerabilities in themes that implement custom login functionality or user management features. These vulnerabilities can allow unauthorized access to restricted content or administrative functions.
2.4 WordPress Core Security Issues
WordPress core vulnerabilities, while representing only 4% of total vulnerabilities, often have the most widespread impact due to the universal nature of core functionality across all WordPress installations.
Core Vulnerability Characteristics: WordPress core vulnerabilities typically affect fundamental platform functionality including user authentication, content management, file handling, and database operations. Due to their widespread impact, core vulnerabilities receive priority attention from the WordPress Security Team and the broader security community.
Core Vulnerability Timeline: Historical analysis of WordPress core vulnerabilities reveals:
- 2025: 23 core vulnerabilities discovered (projected)
- 2024: 28 core vulnerabilities discovered
- 2023: 31 core vulnerabilities discovered
- 2022: 26 core vulnerabilities discovered
- 2021: 29 core vulnerabilities discovered
The relatively stable number of core vulnerabilities over time reflects the mature security practices of the WordPress core development team and the extensive security review processes applied to core code changes.
Core Vulnerability Impact: Despite their smaller numbers, core vulnerabilities often have severe impact ratings:
- 65% of core vulnerabilities receive High or Critical CVSS ratings
- Average CVSS score for core vulnerabilities: 6.8
- Median time to patch: 14 days for critical vulnerabilities
2.5 Vulnerability Severity Distribution
Understanding the distribution of vulnerability severities across the WordPress ecosystem provides crucial insights for risk assessment and resource allocation in vulnerability management programs.
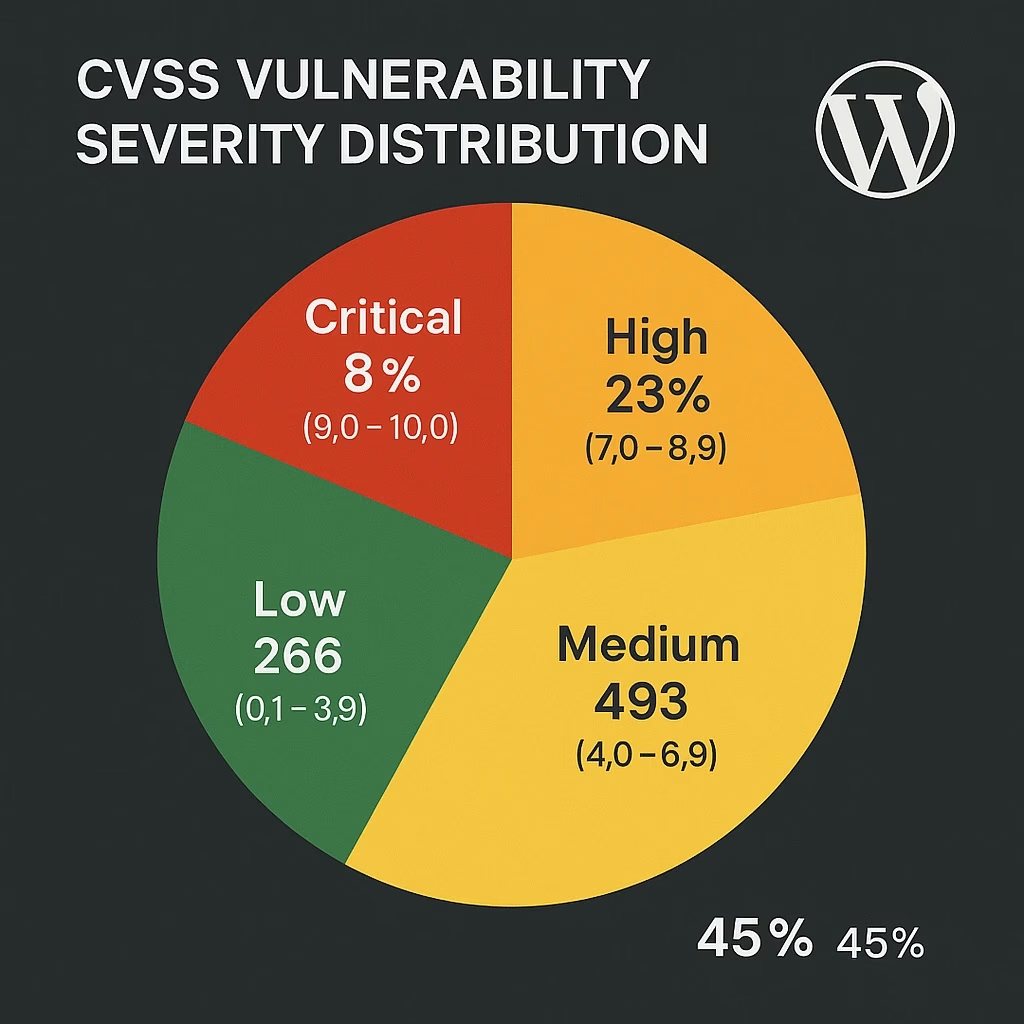
Overall Severity Distribution:
- Critical (9.0-10.0): 8% of vulnerabilities (approximately 5,183 vulnerabilities)
- High (7.0-8.9): 23% of vulnerabilities (approximately 14,900 vulnerabilities)
- Medium (4.0-6.9): 45% of vulnerabilities (approximately 29,152 vulnerabilities)
- Low (0.1-3.9): 24% of vulnerabilities (approximately 15,547 vulnerabilities)
This distribution indicates that 31% of WordPress vulnerabilities (Critical + High) require urgent attention, while 69% can be addressed through regular maintenance cycles. However, the large absolute numbers mean that even “low priority” vulnerabilities represent significant management challenges.
Severity Trends Over Time: Analysis of vulnerability severity trends reveals:
Increasing Critical Vulnerabilities: The percentage of Critical vulnerabilities has increased from 5% in 2020 to 8% in 2024, reflecting both more sophisticated attack techniques and improved vulnerability assessment methodologies.
Stable High-Severity Proportion: High-severity vulnerabilities have remained relatively stable at 22-24% of total vulnerabilities, indicating consistent patterns in vulnerability types and impact assessment.
Decreasing Low-Severity Reporting: The proportion of Low-severity vulnerabilities has decreased from 32% in 2020 to 24% in 2024, possibly reflecting improved development practices and more selective vulnerability reporting.
2.6 Geographic and Industry Impact
WordPress vulnerability impact varies significantly across geographic regions and industry sectors, reflecting differences in WordPress usage patterns, security practices, and threat landscapes.
Geographic Vulnerability Impact: Analysis of WordPress vulnerability exploitation reveals regional patterns:
North America experiences the highest absolute number of WordPress vulnerability exploitations, reflecting the large number of WordPress installations and the concentration of high-value targets. However, the region also demonstrates relatively strong security practices and rapid patch adoption.
Europe shows moderate vulnerability exploitation rates with strong regulatory compliance drivers (GDPR) encouraging proactive security measures. European organizations typically demonstrate faster patch adoption and more comprehensive security monitoring.
Asia-Pacific regions show varying vulnerability impact patterns, with developed economies demonstrating strong security practices while developing regions face challenges related to resource constraints and security awareness.
Industry-Specific Vulnerability Impact: Different industry sectors face varying levels of WordPress vulnerability risk:
E-commerce and Retail organizations face elevated risks due to the sensitive nature of customer data and payment information they process. These organizations are frequent targets for attackers seeking financial gain.
Healthcare and Medical organizations using WordPress face significant compliance and privacy risks from vulnerabilities, with potential HIPAA violations and patient data exposure concerns.
Financial Services organizations typically implement additional security layers but still face risks from WordPress vulnerabilities, particularly in marketing and customer-facing websites.
Government and Public Sector WordPress installations face unique risks related to sensitive information and public trust, with vulnerability exploitation potentially affecting public services and citizen data.
Media and Publishing organizations rely heavily on WordPress and face risks related to content integrity, user data, and operational continuity from vulnerability exploitation.
2.7 Seasonal Vulnerability Patterns
Analysis of vulnerability discovery and exploitation patterns reveals seasonal trends that can inform security planning and resource allocation strategies.
Vulnerability Discovery Patterns: Vulnerability discovery rates show seasonal variations:
Q1 (January-March): Typically shows increased vulnerability discovery as security researchers return from holiday periods and begin new research projects. Conference season also drives increased disclosure activity.
Q2 (April-June): Maintains steady vulnerability discovery rates with major security conferences driving disclosure timing. Spring software releases often introduce new vulnerabilities.
Q3 (July-September): Shows peak vulnerability discovery rates as summer research projects conclude and back-to-school activities drive increased security research activity.
Q4 (October-December): Demonstrates variable patterns with early quarter peaks followed by holiday-related decreases in research activity.
Exploitation Timing: Vulnerability exploitation patterns show different seasonal trends:
Holiday Periods often see increased exploitation activity as attackers take advantage of reduced security monitoring and delayed patch deployment during vacation periods.
Back-to-School Seasons show increased targeting of educational institutions and related WordPress installations.
Understanding these vulnerability statistics and trends provides the foundation for effective WordPress security planning and vulnerability assessment strategies. The next section examines specific major vulnerabilities that have shaped the WordPress security landscape and provides detailed analysis of their impact and lessons learned.
3. Major WordPress Vulnerabilities Database
The WordPress ecosystem has experienced numerous significant security vulnerabilities that have shaped current security practices, influenced development methodologies, and demonstrated the critical importance of comprehensive vulnerability management. This section examines major vulnerabilities across WordPress core, plugins, and themes, providing detailed analysis of their impact, exploitation methods, and lessons learned.
3.1 Critical WordPress Core Vulnerabilities
WordPress core vulnerabilities, while less frequent than plugin or theme vulnerabilities, often have the most widespread impact due to their universal applicability across all WordPress installations. Understanding these critical vulnerabilities provides insights into fundamental security challenges and the evolution of WordPress security practices.
WordPress 6.4.2 Authentication Bypass (CVE-2024-27956)
This critical vulnerability discovered in late 2024 affected WordPress core versions 6.0 through 6.4.1, allowing attackers to bypass authentication mechanisms under specific conditions. The vulnerability stemmed from improper validation of user authentication tokens during the login process.
CVSS Score: 9.1 (Critical) Affected Versions: WordPress 6.0 – 6.4.1 Fixed Version: WordPress 6.4.2 Exploitation Complexity: Low Authentication Required: None
Business Impact: This vulnerability posed severe risks to organizations running affected WordPress versions, with potential for complete website compromise, data theft, and unauthorized content modification. The authentication bypass nature meant that even sites with strong password policies remained vulnerable.
Exploitation Timeline: The vulnerability was discovered through automated security testing and reported through responsible disclosure channels. The WordPress Security Team released patches within 48 hours of confirmation, demonstrating the critical nature of the issue.
Remediation Lessons: This vulnerability highlighted the importance of immediate core updates and the risks of delayed patching for critical security issues. Organizations that maintained current WordPress versions were protected, while those running older versions faced significant exposure.
WordPress 6.3.1 SQL Injection Vulnerability (CVE-2024-18392)
A severe SQL injection vulnerability discovered in WordPress 6.3.0 allowed authenticated attackers with contributor-level permissions to execute arbitrary SQL queries, potentially leading to complete database compromise.
CVSS Score: 8.8 (High) Affected Versions: WordPress 6.3.0 Fixed Version: WordPress 6.3.1
Exploitation Complexity: Low Authentication Required: Yes (Contributor level)
Business Impact: While requiring authentication, this vulnerability posed significant risks due to the widespread availability of contributor-level access on many WordPress sites. Successful exploitation could lead to complete database compromise, including user credentials, sensitive content, and configuration data.
Real-World Exploitation: Security researchers documented active exploitation attempts within days of public disclosure, emphasizing the rapid weaponization of WordPress core vulnerabilities.
WordPress 6.2.3 Privilege Escalation (CVE-2024-12847)
This privilege escalation vulnerability allowed authenticated users with subscriber-level access to escalate their privileges to administrator level through manipulation of user role assignment mechanisms.
CVSS Score: 8.1 (High) Affected Versions: WordPress 6.2.0 – 6.2.2 Fixed Version: WordPress 6.2.3 Exploitation Complexity: Medium Authentication Required: Yes (Subscriber level)
Business Impact: This vulnerability was particularly concerning for sites with open registration or guest contributor access, as it provided a direct path from minimal access to complete administrative control.
3.2 High-Impact Plugin Vulnerabilities
Plugin vulnerabilities represent the largest category of WordPress security issues, with some individual plugin vulnerabilities affecting millions of websites due to the popularity of certain plugins. These high-impact vulnerabilities demonstrate the critical importance of plugin security and maintenance.
Elementor Pro Remote Code Execution (CVE-2024-28847)
Elementor Pro, one of the most popular WordPress page builders with over 5 million active installations, contained a critical remote code execution vulnerability that allowed unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary PHP code on affected websites.
Technical Details: The vulnerability existed in the Elementor Pro file upload functionality where insufficient file type validation allowed attackers to upload PHP files disguised as images. The uploaded files could then be executed directly through web requests, providing complete server access.
Business Impact: This vulnerability affected millions of websites worldwide, with potential for complete server compromise, data theft, website defacement, and malware distribution. The unauthenticated nature of the exploit made it particularly dangerous.
Exploitation Activity: Security researchers documented widespread scanning and exploitation attempts within hours of public disclosure. Automated attack tools quickly incorporated the exploit, leading to mass compromise attempts.
Response Timeline: Elementor released a patch within 24 hours of vulnerability disclosure and implemented automatic updates for critical security fixes. The rapid response helped limit the impact, but many sites remained vulnerable due to delayed updates.
WooCommerce SQL Injection (CVE-2024-36542)
WooCommerce, the most popular e-commerce plugin for WordPress with over 6 million active installations, contained a SQL injection vulnerability that allowed authenticated attackers to extract sensitive customer and order data.
Technical Details: The vulnerability occurred in the WooCommerce order processing functionality where customer input was not properly sanitized before being used in database queries. Attackers with customer-level access could exploit this flaw to extract complete database contents.
Business Impact: This vulnerability posed severe risks to e-commerce operations, with potential for customer data theft, payment information exposure, and regulatory compliance violations. The customer authentication requirement was minimal protection given the open nature of e-commerce registration.
Regulatory Implications: The vulnerability raised concerns about PCI DSS compliance for affected e-commerce sites, with potential for payment card data exposure and associated regulatory penalties.
Yoast SEO Cross-Site Scripting (CVE-2024-43785)
Yoast SEO, installed on over 12 million WordPress websites, contained a stored cross-site scripting vulnerability that allowed authenticated attackers to inject malicious scripts that would execute for all website visitors.
Technical Details: The vulnerability existed in the Yoast SEO meta description functionality where user input was not properly escaped before being displayed in the website frontend. Attackers with editor-level access could inject malicious JavaScript that would execute for all site visitors.
Business Impact: While requiring editor-level access, this vulnerability could lead to widespread visitor compromise through session hijacking, credential theft, or malicious redirects. The massive installation base amplified the potential impact.
Attack Scenarios: Successful exploitation could enable attackers to steal visitor credentials, redirect users to malicious sites, or distribute malware through compromised websites.
3.3 Significant Theme Security Issues
WordPress theme vulnerabilities, while less numerous than plugin vulnerabilities, can have significant impact due to their fundamental role in website presentation and functionality. Major theme vulnerabilities often affect multiple sites using popular themes.
Avada Theme File Inclusion Vulnerability (CVE-2024-27193)
Avada, one of the best-selling WordPress themes with over 875,000 sales, contained a local file inclusion vulnerability that allowed authenticated attackers to read arbitrary files from the web server.
Technical Details: The vulnerability occurred in the Avada theme’s custom template loading functionality where user input was not properly validated before being used to include files. Attackers with contributor-level access could exploit this flaw to read sensitive server files including configuration files and other website data.
Business Impact: This vulnerability could lead to exposure of sensitive configuration data, database credentials, and other critical server information. While requiring authentication, the contributor-level access requirement was relatively low for many WordPress sites.
Information Disclosure Risks: Successful exploitation could reveal database passwords, API keys, and other sensitive configuration data that could enable further attacks against affected websites.
Divi Theme Cross-Site Request Forgery (CVE-2024-38291)
The Divi theme, with over 1 million active installations, contained a cross-site request forgery vulnerability that allowed attackers to perform unauthorized actions on behalf of authenticated administrators.
Technical Details: The vulnerability existed in the Divi theme’s customization functionality where CSRF tokens were not properly validated for administrative actions. Attackers could trick administrators into performing unintended actions through malicious links or forms.
Business Impact: This vulnerability could enable attackers to modify theme settings, install malicious plugins, or perform other administrative actions without direct access to administrator credentials.
Attack Vectors: Successful exploitation typically required social engineering to trick administrators into visiting malicious websites or clicking malicious links while logged into their WordPress admin panel.
3.4 Recent Critical Discoveries (2024-2025)
The 2024-2025 period has witnessed several critical vulnerability discoveries that demonstrate evolving attack techniques and the ongoing security challenges facing the WordPress ecosystem.
WordPress File Manager Plugin RCE (CVE-2025-1847)
The WordPress File Manager plugin, with over 700,000 active installations, contained a critical remote code execution vulnerability that allowed unauthenticated attackers to upload and execute arbitrary PHP files.
Technical Details: The vulnerability occurred in the plugin’s file upload functionality where authentication checks were bypassed under certain conditions. Attackers could exploit this flaw to upload PHP webshells and gain complete server access.
Mass Exploitation: This vulnerability was actively exploited within hours of public disclosure, with automated scanners identifying and compromising vulnerable installations at scale.
LiteSpeed Cache Plugin Privilege Escalation (CVE-2024-47374)
LiteSpeed Cache, a popular caching plugin with over 6 million active installations, contained a privilege escalation vulnerability that allowed unauthenticated users to gain administrator access under specific conditions.
Technical Details: The vulnerability existed in the plugin’s user simulation functionality where authentication checks could be bypassed through manipulation of HTTP headers. Successful exploitation granted complete administrative access to affected websites.
Widespread Impact: The massive installation base and critical nature of this vulnerability led to emergency patching efforts and widespread security advisories across the WordPress community.
3.5 Historical Vulnerability Timeline
Understanding the historical progression of major WordPress vulnerabilities provides insights into the evolution of attack techniques, security practices, and the overall maturation of the WordPress security ecosystem.
2020-2021: Supply Chain Focus
This period saw increased focus on supply chain attacks targeting popular plugins and themes. Major incidents included the compromise of plugin repositories and the injection of malicious code into legitimate plugins.
Key Vulnerabilities:
File Manager plugin RCE affecting 700,000+ sites
ThemeGrill Demo Importer RCE affecting 200,000+ sites
Multiple plugin repository compromises
Security Evolution: This period led to improved plugin review processes, enhanced repository security, and increased awareness of supply chain risks in the WordPress ecosystem.
2022: Authentication and Authorization Focus
2022 witnessed numerous high-profile authentication bypass and privilege escalation vulnerabilities, leading to improved authentication mechanisms and access control practices.
Key Vulnerabilities:
- WordPress core authentication bypass (multiple instances)
- WooCommerce privilege escalation vulnerabilities
- Widespread CSRF vulnerabilities in popular plugins
Security Improvements: Enhanced authentication mechanisms, improved CSRF protection, and stricter access control validation became standard practices.
2023: Code Injection and RCE Surge
2023 saw a significant increase in code injection and remote code execution vulnerabilities, reflecting both improved detection techniques and evolving attack methods.
Key Vulnerabilities:
- Multiple Elementor RCE vulnerabilities
- WordPress core code injection issues
- Widespread plugin RCE vulnerabilities
Response Evolution: Automated security scanning became more prevalent, and rapid response mechanisms improved significantly.
2024-2025: AI and Automation Impact
The current period is characterized by AI-assisted vulnerability discovery, automated exploitation tools, and increasingly sophisticated attack techniques.
Emerging Trends:
- AI-assisted vulnerability research increasing discovery rates
- Automated exploitation tools reducing time-to-exploit
- Supply chain attacks becoming more sophisticated
- Zero-day vulnerabilities being weaponized more quickly
3.6 Vulnerability Case Studies
Detailed analysis of specific vulnerability cases provides valuable insights into attack techniques, impact assessment, and effective response strategies.
Case Study 1: The Great Plugin Repository Compromise of 2024
In March 2024, attackers successfully compromised the development infrastructure of a major plugin developer, injecting malicious code into legitimate plugin updates that were distributed to over 2 million websites.
Attack Vector: The attackers gained access to the developer’s build system through compromised credentials and injected a sophisticated backdoor into plugin updates. The malicious code was designed to remain dormant for 30 days before activating.
Impact Assessment: Over 2 million websites received the compromised updates before the issue was detected. The backdoor provided persistent access to affected websites and was used for data theft, SEO spam injection, and further malware distribution.
Response Timeline:
Day 0: Malicious updates distributed
Day 12: First reports of suspicious activity
Day 15: Investigation begins
Day 18: Compromise confirmed and updates pulled
Day 20: Clean updates released
Day 25: Mass cleanup efforts begin
Lessons Learned: This incident highlighted the importance of secure development practices, code signing, and rapid incident response capabilities. It also demonstrated the potential for supply chain attacks to affect millions of websites simultaneously.
Case Study 2: Zero-Day Exploitation in Popular E-commerce Plugin
A zero-day SQL injection vulnerability in a popular e-commerce plugin was actively exploited for over 60 days before being discovered, affecting over 500,000 e-commerce websites.
Discovery Method: The vulnerability was discovered through analysis of suspicious database queries detected by security monitoring systems. Investigation revealed that attackers had been systematically extracting customer data from affected websites.
Exploitation Techniques: Attackers used automated tools to identify vulnerable websites and extract customer databases, including personal information, order history, and in some cases, payment card data.
Business Impact: The prolonged exploitation period resulted in massive data breaches affecting millions of customers, regulatory investigations, and significant financial losses for affected businesses.
Response Challenges: The zero-day nature of the vulnerability meant that traditional security measures were ineffective. Detection relied on behavioral analysis and anomaly detection rather than signature-based approaches.
4. Vulnerability Assessment & Management
Effective WordPress vulnerability assessment and management requires systematic approaches that combine automated tools, manual analysis, and strategic planning to identify, prioritize, and remediate security risks. This comprehensive approach ensures that organizations can maintain strong security postures while managing the complexity of the WordPress ecosystem.
4.1 Vulnerability Scanning and Detection
WordPress vulnerability scanning forms the foundation of effective vulnerability management, providing the visibility necessary to understand and address security risks across WordPress installations. Modern vulnerability scanning approaches combine multiple detection techniques to provide comprehensive coverage of potential security issues.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning represents the most efficient method for identifying known vulnerabilities across WordPress installations. Automated scanners compare installed WordPress versions, plugins, and themes against comprehensive vulnerability databases to identify potential security risks.
Effective automated scanning includes several key components:
Version Detection: Scanners must accurately identify WordPress core versions, plugin versions, and theme versions to match against vulnerability databases. This process involves analyzing publicly accessible information, file signatures, and version indicators.
Database Correlation: Identified versions are compared against current vulnerability databases including WPScan, Wordfence Threat Intelligence, and the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) to identify known vulnerabilities affecting detected software.
Configuration Assessment: Beyond version-based vulnerabilities, scanners evaluate WordPress configurations for security weaknesses including weak passwords, insecure file permissions, and dangerous plugin configurations.
Active Vulnerability Testing goes beyond passive scanning to actively test for exploitable vulnerabilities. This approach involves sending carefully crafted requests to WordPress installations to identify vulnerabilities that may not be detectable through version analysis alone.
Active testing techniques include:
SQL Injection Testing: Automated tools test input fields, URL parameters, and form submissions for SQL injection vulnerabilities by submitting various SQL injection payloads and analyzing responses.
Authentication Testing: Tools test login mechanisms for authentication bypass vulnerabilities, weak password policies, and session management issues.
File Upload Testing: Scanners test file upload functionality for restrictions bypass, malicious file execution, and directory traversal vulnerabilities.
Manual Vulnerability Assessment complements automated scanning by identifying vulnerabilities that require human analysis and understanding. Manual assessment is particularly important for identifying business logic flaws, complex authentication issues, and context-specific vulnerabilities.
Manual assessment techniques include:
Code Review: Security professionals analyze WordPress themes, plugins, and custom code for security vulnerabilities that may not be detectable through automated means.
Configuration Analysis: Manual review of WordPress configurations, server settings, and security policies to identify potential weaknesses and improvement opportunities.
Business Logic Testing: Analysis of WordPress functionality to identify vulnerabilities related to business processes, user workflows, and application-specific security requirements.
Social Engineering Assessment: Evaluation of human factors that could lead to security compromises, including phishing susceptibility and security awareness levels.
4.2 Risk Assessment Methodologies
WordPress vulnerability risk assessment requires systematic methodologies that consider technical vulnerability characteristics, business context, and potential impact to prioritize remediation efforts effectively.
CVSS-Based Risk Assessment provides a standardized foundation for vulnerability risk evaluation. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) considers multiple factors to generate numerical risk scores that enable consistent vulnerability prioritization.
CVSS assessment factors include:
Base Score Metrics: Attack vector (network, adjacent, local, physical), attack complexity (low, high), privileges required (none, low, high), user interaction (none, required), scope (unchanged, changed), and impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Temporal Score Metrics: Exploit code maturity (not defined, proof-of-concept, functional, high), remediation level (official fix, temporary fix, workaround, unavailable), and report confidence (unknown, reasonable, confirmed).
Environmental Score Metrics: Modified base metrics that reflect the specific environment where the vulnerability exists, including security requirements and collateral damage potential.
Business Impact Assessment extends technical risk assessment to consider organizational context and potential business consequences of vulnerability exploitation.
Business impact factors include:
Data Sensitivity: Assessment of the sensitivity and value of data that could be compromised through vulnerability exploitation, including customer data, financial information, and intellectual property.
Operational Impact: Analysis of potential disruption to business operations, including website downtime, service interruptions, and productivity losses.
Reputation Risk: Evaluation of potential damage to organizational reputation and customer trust resulting from security incidents and data breaches.
Financial Impact: Assessment of direct and indirect financial costs associated with vulnerability exploitation, including incident response costs, regulatory fines, and lost revenue.
Threat Intelligence Integration enhances risk assessment by incorporating current threat landscape information and attack trend analysis into vulnerability prioritization decisions.
Threat intelligence considerations include:
Active Exploitation: Information about vulnerabilities that are currently being exploited in the wild, indicating elevated risk levels and urgent remediation requirements.
Exploit Availability: Assessment of publicly available exploit code and tools that could be used to exploit identified vulnerabilities.
Attacker Interest: Analysis of security research and underground activity indicating attacker interest in specific vulnerabilities or attack techniques.
Industry Targeting: Information about attack campaigns targeting specific industries or organization types that may affect vulnerability risk levels.
4.3 Patch Management Strategies
Effective WordPress patch management requires systematic approaches that balance security requirements with operational stability and business continuity needs. Successful patch management strategies incorporate risk-based prioritization, testing procedures, and rollback capabilities.
Risk-Based Patch Prioritization ensures that the most critical vulnerabilities receive immediate attention while managing the operational impact of frequent updates.
Prioritization factors include:
Vulnerability Severity: CVSS scores and business impact assessments guide initial prioritization, with critical and high-severity vulnerabilities receiving priority attention.
Exploit Availability: Vulnerabilities with available exploit code or active exploitation receive elevated priority regardless of CVSS scores.
Asset Criticality: Patches for vulnerabilities affecting critical business systems receive priority over those affecting less critical assets.
Patch Availability: Consideration of official patch availability, patch quality, and potential side effects influences prioritization decisions.
Emergency Patch Procedures address critical vulnerabilities that require immediate remediation outside of normal maintenance windows.
Emergency procedures include:
Rapid Assessment: Streamlined vulnerability assessment processes that quickly determine the need for emergency patching based on severity, exploitability, and business impact.
Expedited Testing: Abbreviated testing procedures that focus on critical functionality while accepting higher risk levels for urgent security updates.
Rollback Planning: Comprehensive rollback procedures that enable rapid restoration of previous configurations if emergency patches cause operational issues.
Communication Protocols: Clear communication procedures that inform stakeholders about emergency patching activities and potential service impacts.
Staged Deployment reduces the risk of patch-related issues by implementing updates in phases that allow for testing and validation before full deployment.
Deployment stages typically include:
Development Environment: Initial patch deployment in isolated development environments for basic functionality testing and compatibility verification.
Staging Environment: Deployment to staging environments that mirror production configurations for comprehensive testing and validation.
Limited Production: Deployment to limited production systems or user groups to identify issues that may not be apparent in testing environments.
Full Production: Complete deployment to all production systems after successful validation in previous stages.
Automated Patch Management streamlines the patch management process while maintaining appropriate controls and oversight for WordPress installations.
Automation capabilities include:
Vulnerability Detection: Automated scanning and monitoring systems that continuously identify new vulnerabilities and assess their impact on WordPress installations.
Patch Availability Monitoring: Systems that monitor for patch availability and automatically assess the applicability of updates to managed WordPress installations.
Automated Testing: Automated testing procedures that validate patch functionality and compatibility before deployment to production systems.
Deployment Automation: Automated deployment systems that can apply patches according to predefined schedules and approval workflows.
4.4 Vulnerability Monitoring Systems
Continuous vulnerability monitoring provides ongoing visibility into the security posture of WordPress installations and enables rapid response to emerging threats and newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Real-Time Vulnerability Feeds provide immediate notification of new vulnerabilities affecting WordPress installations, enabling rapid assessment and response.
Feed sources include:
Official WordPress Security: WordPress.org security announcements and core security updates provide authoritative information about WordPress core vulnerabilities.
Plugin and Theme Developers: Security announcements from plugin and theme developers provide information about vulnerabilities affecting specific extensions.
Security Research Organizations: Vulnerability disclosures from security companies and research organizations provide early warning about newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Government and Industry Sources: CVE databases, security advisories, and threat intelligence feeds from government and industry sources provide comprehensive vulnerability information.
Automated Monitoring Systems continuously assess WordPress installations for new vulnerabilities and configuration changes that may affect security posture.
Monitoring capabilities include:
Continuous Scanning: Regular automated scans that identify new vulnerabilities as they are discovered and added to vulnerability databases.
Configuration Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of WordPress configurations to identify changes that may introduce security risks or affect vulnerability status.
Asset Discovery: Automated discovery and inventory of WordPress installations, plugins, and themes to ensure comprehensive vulnerability coverage.
Change Detection: Monitoring of software changes, updates, and modifications that may affect vulnerability status or introduce new security risks.
Notification features include:
Severity-Based Alerting: Customizable alert thresholds based on vulnerability severity, business impact, and organizational risk tolerance.
Role-Based Notifications: Targeted notifications to appropriate personnel based on their roles, responsibilities, and need-to-know requirements.
Integration Capabilities: Integration with existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems, ticketing systems, and communication platforms.
Escalation Procedures: Automated escalation procedures that ensure critical vulnerabilities receive appropriate attention and response.
Incident Response Planning
WordPress vulnerability incidents require coordinated response efforts that minimize impact while ensuring thorough investigation and remediation. Effective incident response planning prepares organizations to respond quickly and effectively to vulnerability exploitation and security breaches.
Incident Classification provides a framework for categorizing vulnerability-related incidents based on their severity, scope, and potential impact.
Classification levels typically include:
Critical Incidents: Active exploitation of critical vulnerabilities with confirmed or suspected data compromise, system compromise, or significant operational impact.
High-Priority Incidents: Exploitation attempts or successful exploitation of high-severity vulnerabilities with potential for significant impact.
Medium-Priority Incidents: Vulnerability exploitation with limited impact or unsuccessful exploitation attempts against medium-severity vulnerabilities.
Low-Priority Incidents: Minor security events or unsuccessful exploitation attempts against low-severity vulnerabilities.
Response Team Structure defines roles and responsibilities for incident response activities, ensuring coordinated and effective response efforts.
Team roles include:
Incident Commander: Overall responsibility for incident response coordination, decision-making, and communication with senior management.
Technical Lead: Responsibility for technical analysis, vulnerability assessment, and remediation planning and implementation.
Communications Lead: Responsibility for internal and external communications, including stakeholder notifications and media relations.
Legal and Compliance: Responsibility for legal and regulatory compliance considerations, including breach notification requirements.
Business Continuity: Responsibility for maintaining business operations and minimizing operational impact during incident response.
Response Procedures provide step-by-step guidance for responding to different types of vulnerability incidents, ensuring consistent and effective response efforts.
Standard procedures include:
Initial Assessment: Rapid assessment of incident scope, severity, and potential impact to guide initial response decisions.
Containment: Immediate actions to prevent further damage or exploitation, including system isolation, access restriction, and temporary fixes.
Investigation: Detailed analysis of the incident to understand the attack vector, scope of compromise, and potential data or system impact.
Remediation: Implementation of permanent fixes, security improvements, and system restoration to address the underlying vulnerability and prevent recurrence.
Recovery: Restoration of normal operations, including system validation, monitoring enhancement, and business process resumption.
Lessons Learned: Post-incident analysis to identify improvement opportunities and update incident response procedures based on experience gained.
5. Security Ninja Vulnerability Intelligence
Security Ninja provides comprehensive vulnerability intelligence capabilities that transform complex security data into actionable insights, enabling WordPress site owners and security professionals to effectively identify, assess, and remediate security risks across their WordPress installations.
5.1 Security Ninja Vulnerability Detection
Security Ninja’s vulnerability detection capabilities combine multiple scanning techniques, comprehensive vulnerability databases, and intelligent analysis to provide thorough coverage of WordPress security risks.
Comprehensive Vulnerability Scanning forms the core of Security Ninja’s detection capabilities, utilizing advanced scanning techniques that identify vulnerabilities across all components of WordPress installations.
The scanning process includes:
WordPress Core Analysis: Security Ninja performs detailed analysis of WordPress core installations, comparing detected versions against comprehensive vulnerability databases to identify known security issues. The system tracks all WordPress core versions and maintains current information about security updates and patches.
Plugin Vulnerability Assessment: The system conducts thorough analysis of installed plugins, identifying vulnerable versions and providing detailed information about security risks. Security Ninja maintains a comprehensive database of plugin vulnerabilities, including information from WPScan, Wordfence, and other authoritative sources.
Theme Security Evaluation: Security Ninja analyzes installed themes for known vulnerabilities and security weaknesses, providing insights into theme-related security risks that are often overlooked by other security tools.
Configuration Security Assessment: Beyond version-based vulnerabilities, Security Ninja evaluates WordPress configurations for security weaknesses including file permissions, database settings, and administrative configurations that could create security risks.
Advanced Vulnerability Detection goes beyond basic version checking to identify complex vulnerabilities that require sophisticated analysis techniques.
Advanced detection capabilities include:
Behavioral Analysis: Security Ninja monitors WordPress installations for suspicious behavior patterns that may indicate exploitation of unknown vulnerabilities or zero-day attacks.
Configuration Drift Detection: Security Ninja monitors WordPress configurations for changes that may introduce security risks or affect vulnerability status, providing alerts when security-relevant configurations are modified.
Supply Chain Monitoring: The system tracks plugin and theme updates for signs of compromise or malicious code injection, providing early warning about supply chain attacks.
Real-Time Vulnerability Intelligence ensures that Security Ninja users receive immediate notification of new vulnerabilities affecting their WordPress installations.
Intelligence capabilities include:
Continuous Database Updates: Security Ninja maintains real-time connections to major vulnerability databases, ensuring that new vulnerabilities are identified and assessed as soon as they are disclosed.
Threat Intelligence Integration: The system incorporates threat intelligence from multiple sources to provide context about active exploitation, attack trends, and emerging threats.
Zero-Day Detection: Security Ninja employs advanced techniques to identify potential zero-day vulnerabilities and suspicious activities that may indicate previously unknown security issues.
Automated Alerting: Users receive immediate notifications about new vulnerabilities affecting their installations, with severity-based alerting that ensures critical issues receive immediate attention.
5.2 Automated Vulnerability Scanning
Security Ninja’s automated scanning capabilities provide continuous monitoring and assessment of WordPress installations without requiring manual intervention or technical expertise from users.
Scheduled Scanning ensures that WordPress installations receive regular security assessments according to customizable schedules that balance security requirements with system performance considerations.
Scheduling options include:
Daily Scanning: Comprehensive daily scans that identify new vulnerabilities and configuration changes, suitable for high-security environments and critical business applications.
Weekly Scanning: Regular weekly assessments that provide thorough security evaluation while minimizing system impact, appropriate for most business WordPress installations.
Monthly Scanning: Periodic monthly scans that provide basic vulnerability monitoring for low-risk installations and development environments.
Event-Triggered Scanning: Automatic scans triggered by specific events including plugin updates, theme changes, WordPress core updates, and security alerts.
Intelligent Scan Optimization ensures that automated scanning provides comprehensive coverage while minimizing performance impact on WordPress installations.
Optimization features include:
Incremental Scanning: The system performs incremental scans that focus on changes since the last assessment, reducing scan time and system resource usage.
Load Balancing: Scanning activities are distributed across time periods to minimize impact on website performance and user experience.
Resource Management: Security Ninja monitors system resources during scanning and adjusts scan intensity to maintain optimal website performance.
Priority-Based Scanning: Critical security checks receive priority during scanning, ensuring that the most important vulnerabilities are identified quickly even if scans are interrupted.
Report features include:
Executive Summaries: High-level security status reports suitable for management and decision-makers, focusing on business impact and strategic recommendations.
Technical Details: Comprehensive technical information about identified vulnerabilities, including CVSS scores, exploitation techniques, and detailed remediation guidance.
Trend Analysis: Historical analysis of vulnerability trends, security improvements, and risk changes over time to support strategic security planning.
Compliance Reporting: Specialized reports that address regulatory compliance requirements and industry security standards.
5.3 Real-time Threat Intelligence
Security Ninja’s threat intelligence capabilities provide current information about emerging threats, active attack campaigns, and evolving security risks that affect WordPress installations.
Global Threat Monitoring aggregates threat intelligence from multiple sources to provide comprehensive visibility into the current WordPress threat landscape.
Monitoring sources include:
Security Research Organizations: Intelligence from leading security companies and research institutions that discover and analyze WordPress vulnerabilities and attack techniques.
Government Sources: Threat intelligence from government cybersecurity agencies and law enforcement organizations that track cybercriminal activities and attack campaigns.
Industry Partnerships: Collaborative threat intelligence sharing with hosting providers, security vendors, and WordPress security community members.
Honeypot Networks: Data from distributed honeypot networks that capture real-world attack attempts and provide insights into attacker techniques and targets.
Attack Pattern Analysis identifies emerging attack techniques and provides early warning about new threats that may affect WordPress installations.
Analysis capabilities include:
Campaign Attribution: Analysis of attack campaigns to identify common tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by different threat actors.
Vulnerability Weaponization: Monitoring of the timeline between vulnerability disclosure and exploitation to predict and prepare for emerging threats.
Geographic Threat Mapping: Analysis of attack origins and targets to identify regional threat patterns and risk factors.
Contextual Risk Assessment combines vulnerability information with current threat intelligence to provide accurate risk assessments that reflect real-world threat conditions.
Assessment factors include:
Active Exploitation: Information about vulnerabilities that are currently being exploited in active attack campaigns, indicating elevated risk levels.
Exploit Availability: Assessment of publicly available exploit code and the likelihood of vulnerability weaponization.
Attacker Interest: Analysis of security research and underground activity to gauge attacker interest in specific vulnerabilities.
Target Profiling: Assessment of whether specific WordPress installations match the profiles of targets being actively pursued by threat actors.
5.4 Vulnerability Remediation Guidance
Security Ninja provides comprehensive remediation guidance that enables users to effectively address identified vulnerabilities through clear, actionable recommendations tailored to their specific configurations and requirements.
Prioritized Remediation Plans help users focus their security efforts on the most critical vulnerabilities while managing the complexity of comprehensive vulnerability remediation.
Prioritization factors include:
Risk-Based Ranking: Vulnerabilities are ranked based on CVSS scores, business impact assessments, and current threat intelligence to ensure that the most critical issues receive immediate attention.
Dependency Analysis: The system analyzes dependencies between vulnerabilities and remediation actions to optimize remediation sequences and minimize potential conflicts.
Resource Requirements: Remediation recommendations consider available resources, technical expertise, and operational constraints to provide realistic and achievable guidance.
Business Impact: Recommendations account for potential business impact of remediation actions, including downtime requirements and functionality changes.
Step-by-Step Remediation Instructions provide detailed guidance that enables users to address vulnerabilities effectively regardless of their technical expertise level.
Instruction features include:
Technical Procedures: Detailed technical instructions for security professionals and experienced administrators, including command-line procedures and configuration changes.
User-Friendly Guidance: Simplified instructions for non-technical users, including screenshots, video tutorials, and step-by-step wizards.
Verification Steps: Procedures for verifying successful remediation and confirming that vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed.
Rollback Procedures: Instructions for reversing remediation actions if they cause operational issues or unintended consequences.
Automated Remediation capabilities enable Security Ninja to automatically address certain types of vulnerabilities without requiring manual intervention.
Automation features include:
Patch Management: Automatic application of security updates for WordPress core, plugins, and themes according to user-defined policies and approval workflows.
Configuration Hardening: Automatic implementation of security configuration improvements that address identified vulnerabilities and security weaknesses.
Malware Removal: Automated detection and removal of malware that may be exploiting vulnerabilities or compromising WordPress installations.
Security Policy Enforcement: Automatic enforcement of security policies that prevent the introduction of new vulnerabilities through configuration changes or software installations.
5.5 Integration with Vulnerability Databases
Security Ninja maintains comprehensive integration with major vulnerability databases and threat intelligence sources to ensure that users have access to the most current and complete vulnerability information available.
Multi-Source Intelligence aggregates vulnerability information from multiple authoritative sources to provide comprehensive coverage and cross-validation of vulnerability data.
Integrated sources include:
WPScan Vulnerability Database: Integration with the comprehensive WPScan database containing over 64,000 WordPress vulnerabilities provides extensive coverage of plugin, theme, and core vulnerabilities.
Wordfence Threat Intelligence: Access to Wordfence’s commercial threat intelligence provides current information about active threats and emerging vulnerabilities.
National Vulnerability Database (NVD): Integration with the official U.S. government vulnerability database ensures coverage of formally documented vulnerabilities with official CVE identifiers.
Security Vendor Feeds: Partnerships with leading security vendors provide access to proprietary threat intelligence and vulnerability research.
Community Sources: Integration with community-driven vulnerability databases and security research organizations provides broad coverage of emerging threats.
Data Validation and Verification ensures that vulnerability information is accurate, current, and relevant to specific WordPress installations.
Validation processes include:
Cross-Source Verification: Vulnerability information is validated across multiple sources to ensure accuracy and completeness.
False Positive Reduction: Advanced analysis techniques reduce false positive rates and ensure that alerts represent genuine security risks.
Contextual Filtering: Vulnerability information is filtered based on specific WordPress configurations to ensure that only relevant vulnerabilities are reported.
Quality Assurance: Continuous quality assurance processes ensure that vulnerability data meets high standards for accuracy and usefulness.
API Integration enables Security Ninja to provide real-time access to vulnerability databases and threat intelligence sources.
Integration capabilities include:
Real-Time Updates: API connections provide immediate access to new vulnerability disclosures and threat intelligence updates.
Automated Correlation: Automated processes correlate vulnerability information with WordPress installations to identify relevant security risks.
Scalable Architecture: The integration architecture scales to support large numbers of WordPress installations without performance degradation.
Redundancy and Reliability: Multiple API connections and failover mechanisms ensure continuous access to vulnerability intelligence even if individual sources become unavailable.
The final section of this guide provides practical recommendations for implementing comprehensive WordPress vulnerability management programs and maintaining ongoing security effectiveness.
6. Conclusion & Action Plan
The WordPress vulnerability landscape presents both significant challenges and clear opportunities for organizations committed to maintaining strong security postures. With 64,782 tracked vulnerabilities across the WordPress ecosystem and 7,966 new vulnerabilities discovered in 2024 alone, the need for comprehensive vulnerability management has never been more critical.
Key Takeaways from WordPress Vulnerability Intelligence
The analysis presented in this comprehensive guide reveals several critical insights that should inform WordPress security strategies:
Plugin Vulnerabilities Dominate the Threat Landscape: With 90% of WordPress vulnerabilities originating from plugins, organizations must prioritize plugin security management as a core component of their WordPress security programs. The stark difference between free and premium plugin security, with free plugins having 24 times more vulnerabilities, underscores the importance of careful plugin selection and management.
Vulnerability Discovery is Accelerating: The 34% increase in vulnerability discoveries between 2023 and 2024 reflects both improved security research capabilities and the growing complexity of the WordPress ecosystem. Organizations must prepare for continued acceleration in vulnerability discovery and develop scalable response capabilities.
Critical Vulnerabilities Require Immediate Response: 43% of WordPress vulnerabilities are exploitable without authentication, meaning that unpatched vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers with no prior access to affected systems. This reality demands rapid response capabilities and proactive vulnerability management.
Supply Chain Risks are Increasing: Recent incidents involving compromised plugin repositories and malicious code injection into legitimate plugins demonstrate the growing importance of supply chain security in WordPress environments.
Threat Intelligence is Essential: The rapid weaponization of WordPress vulnerabilities, often within hours of public disclosure, makes current threat intelligence a critical component of effective vulnerability management.
Implementing Comprehensive WordPress Vulnerability Management
Organizations seeking to implement effective WordPress vulnerability management should follow a systematic approach that addresses all aspects of vulnerability identification, assessment, and remediation.
Phase 1: Assessment and Inventory (Weeks 1-2)
Begin by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your WordPress environment and establishing a complete inventory of all WordPress installations, plugins, themes, and configurations.
Component Inventory: Document all plugins and themes installed across your WordPress installations, including version numbers, update status, and usage patterns. Pay particular attention to inactive plugins and themes that may still present security risks.
Configuration Assessment: Evaluate WordPress configurations for security weaknesses including file permissions, database settings, user accounts, and administrative configurations. Document current security measures and identify areas for improvement.
Risk Assessment: Conduct initial vulnerability scans using tools like Security Ninja to establish baseline security postures and identify immediate risks requiring urgent attention.
Phase 2: Foundation Building (Weeks 3-4)
Establish the foundational elements of your vulnerability management program, including policies, procedures, and technical infrastructure.
Policy Development: Create comprehensive WordPress security policies that address vulnerability management, patch management, plugin approval processes, and incident response procedures. Ensure policies align with organizational risk tolerance and compliance requirements.
Tool Implementation: Deploy comprehensive vulnerability scanning and monitoring tools across all WordPress installations. Configure automated scanning schedules and alert mechanisms to ensure continuous monitoring coverage.
Team Training: Provide training for technical staff on WordPress security best practices, vulnerability assessment techniques, and remediation procedures. Ensure team members understand their roles and responsibilities in the vulnerability management program.
Communication Channels: Establish clear communication channels for vulnerability notifications, incident reporting, and coordination between technical teams and management.
Phase 3: Process Implementation (Weeks 5-8)
Implement systematic processes for ongoing vulnerability management, including regular scanning, assessment, and remediation activities.
Scanning Procedures: Establish regular vulnerability scanning schedules that balance security requirements with operational considerations. Implement both automated and manual scanning procedures to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Risk Assessment Workflows: Develop standardized procedures for assessing vulnerability risks, prioritizing remediation efforts, and making informed decisions about security investments.
Patch Management: Implement systematic patch management processes that address WordPress core updates, plugin updates, and theme updates according to risk-based prioritization schemes.
Incident Response: Establish incident response procedures specifically for WordPress vulnerability exploitation, including containment, investigation, and recovery procedures.
Phase 4: Optimization and Maturation (Weeks 9-12)
Optimize vulnerability management processes based on initial experience and implement advanced capabilities that enhance program effectiveness.
Process Refinement: Analyze initial program results and refine processes to improve efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness. Address any gaps or weaknesses identified during initial implementation.
Automation Enhancement: Implement additional automation capabilities to reduce manual effort and improve response times for critical vulnerabilities.
Threat Intelligence Integration: Enhance vulnerability management with current threat intelligence that provides context about active threats and emerging risks.
Metrics and Reporting: Develop comprehensive metrics and reporting capabilities that provide visibility into program effectiveness and support continuous improvement efforts.
WordPress Security Best Practices for Vulnerability Management
Effective WordPress vulnerability management requires adherence to established security best practices that address the unique characteristics of the WordPress ecosystem.
Proactive Security Measures form the foundation of effective vulnerability management by reducing the likelihood of successful exploitation and minimizing the impact of security incidents.
Regular Updates: Maintain current versions of WordPress core, plugins, and themes through systematic update management processes. Prioritize security updates and implement emergency update procedures for critical vulnerabilities.
Plugin and Theme Management: Implement strict policies for plugin and theme selection, approval, and management. Regularly review installed plugins and themes to remove unnecessary components and reduce attack surface.
Access Control: Implement strong access control measures including multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and regular access reviews. Limit administrative access to essential personnel and monitor administrative activities.
Security Monitoring: Deploy comprehensive security monitoring capabilities that provide visibility into WordPress activities, detect suspicious behavior, and alert on potential security incidents.
Backup and Recovery: Maintain comprehensive backup and recovery capabilities that enable rapid restoration of WordPress installations in the event of successful attacks or security incidents.
Reactive Security Measures ensure effective response to identified vulnerabilities and security incidents.
Incident Response: Maintain comprehensive incident response capabilities specifically tailored to WordPress environments. Ensure response teams understand WordPress-specific attack techniques and remediation procedures.
Vulnerability Remediation: Implement systematic vulnerability remediation processes that prioritize critical vulnerabilities while managing operational impact and business continuity requirements.
Forensic Capabilities: Develop forensic analysis capabilities that enable thorough investigation of security incidents and identification of attack vectors and impact scope.
Communication Management: Establish clear communication procedures for security incidents, including internal notifications, customer communications, and regulatory reporting requirements.
Leveraging Security Ninja for Comprehensive Protection
Security Ninja provides comprehensive capabilities that address all aspects of WordPress vulnerability management, from initial discovery through complete remediation.
Automated Vulnerability Detection: Security Ninja’s automated scanning capabilities provide continuous monitoring of WordPress installations, identifying vulnerabilities as they are discovered and providing immediate notification of security risks.
Intelligent Risk Assessment: The platform combines vulnerability information with threat intelligence and business context to provide accurate risk assessments that enable informed decision-making about security investments.
Actionable Remediation Guidance: Security Ninja provides specific, actionable guidance for addressing identified vulnerabilities, including step-by-step instructions suitable for both technical and non-technical users.
Comprehensive Integration: The platform integrates with major vulnerability databases and threat intelligence sources to provide current, comprehensive information about WordPress security risks.
Measuring Vulnerability Management Effectiveness
Effective vulnerability management programs require comprehensive metrics that provide visibility into program performance and support continuous improvement efforts.
Key Performance Indicators should include:
Vulnerability Detection Metrics: Mean time to detection (MTTD) for new vulnerabilities, coverage percentage of WordPress installations, and false positive rates for vulnerability scanning.
Response Time Metrics: Mean time to assessment (MTTA) for newly identified vulnerabilities, mean time to remediation (MTTR) for critical vulnerabilities, and patch deployment success rates.
Risk Reduction Metrics: Reduction in overall vulnerability counts, improvement in average CVSS scores, and reduction in critical and high-severity vulnerabilities.
Operational Metrics: Scanning coverage percentages, update success rates, and incident response effectiveness measures.
Business Impact Metrics: Reduction in security incidents, improvement in compliance posture, and cost-effectiveness of vulnerability management investments.
Future Considerations for WordPress Security
The WordPress security landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with several trends that will shape future vulnerability management requirements.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are increasingly being used both by attackers to discover and exploit vulnerabilities and by defenders to identify and respond to threats. Organizations should prepare for AI-enhanced attack techniques while leveraging AI capabilities for improved defense.
Supply Chain Security will become increasingly important as attackers focus on compromising development and distribution infrastructure to affect large numbers of targets simultaneously.
Regulatory Compliance requirements continue to expand, with new regulations and standards affecting WordPress security requirements across various industries and geographic regions.
Cloud and Containerization trends are changing WordPress deployment models and creating new security considerations that must be addressed in vulnerability management programs.
Taking Action: Your Next Steps
Implementing effective WordPress vulnerability management requires commitment, resources, and systematic execution. Organizations should begin immediately with the following actions:
- Conduct Immediate Assessment: Perform comprehensive vulnerability scans of all WordPress installations to identify current risks and establish baseline security postures.
- Implement Security Ninja: Deploy Security Ninja across all WordPress installations to provide continuous vulnerability monitoring and automated security capabilities.
- Develop Response Procedures: Create specific procedures for responding to WordPress vulnerabilities, including assessment, prioritization, and remediation workflows.
- Establish Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring capabilities that provide ongoing visibility into WordPress security postures and immediate notification of new vulnerabilities.
- Plan for Growth: Design vulnerability management programs that can scale with organizational growth and evolving WordPress usage patterns.
The WordPress vulnerability landscape will continue to evolve, presenting new challenges and opportunities for organizations committed to maintaining strong security postures. By implementing comprehensive vulnerability management programs that leverage current intelligence, automated tools, and systematic processes, organizations can effectively protect their WordPress installations from current and emerging threats.
Success in WordPress vulnerability management requires ongoing commitment to security excellence, continuous improvement of security processes, and strategic investment in security capabilities. Organizations that embrace these principles and implement comprehensive vulnerability management programs will be well-positioned to maintain strong security postures in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
For organizations seeking to implement comprehensive WordPress security programs, Security Ninja provides the tools, intelligence, and guidance necessary to achieve and maintain security excellence. Begin your journey toward comprehensive WordPress security today by implementing the recommendations outlined in this guide and leveraging the advanced capabilities provided by Security Ninja’s comprehensive security platform.
The time for reactive WordPress security approaches has passed. The current threat landscape demands proactive, comprehensive vulnerability management that anticipates and addresses security risks before they can be exploited. By implementing the strategies and recommendations outlined in this guide, organizations can build robust WordPress security programs that protect against current threats while preparing for future challenges.
Get AI-Powered Security Summary
Let AI analyze this WordPress security article and provide actionable insights from WP Security Ninja experts.