Updated on
WordPress security hardening represents the most effective defense strategy against the escalating threat landscape targeting WordPress websites in 2025. With 7,966 new vulnerabilities discovered in the WordPress ecosystem during 2024 alone, representing a 34% increase over the previous year, implementing comprehensive security hardening measures has become essential for website survival and business continuity.
Security hardening transforms your WordPress installation from a potential target into a fortified digital fortress. Unlike reactive security measures that respond to threats after they occur, hardening implements proactive defenses that prevent attacks before they can compromise your website. This comprehensive approach reduces successful attack rates by 99.7% while improving site performance and reliability by 40%.
The financial impact of inadequate WordPress security extends far beyond immediate technical concerns. Data breaches now cost businesses an average of $4.45 million per incident, while website downtime can result in revenue losses exceeding $5,600 per minute for e-commerce operations. These statistics underscore the critical importance of implementing robust security hardening measures before threats materialize.
Security Ninja provides the most comprehensive WordPress security hardening solution available, combining automated scanning, one-click implementation, and continuous monitoring to deliver enterprise-grade protection for websites of all sizes. This guide demonstrates how to leverage Security Ninja’s advanced capabilities alongside manual hardening techniques to achieve maximum security effectiveness.
Contents
1. Understanding WordPress Security Architecture & Attack Vectors
Plugin and theme layers introduce the highest security risk, representing 90% of all WordPress vulnerabilities discovered in 2024. Third-party developers often lack the security expertise and resources available to the WordPress core team, resulting in code quality variations and security implementation inconsistencies. Popular plugins with millions of installations become high-value targets for attackers seeking maximum impact from single vulnerability exploitations.
The hosting environment and server configuration layer provides the underlying infrastructure supporting WordPress operations. Server misconfigurations, outdated software versions, and inadequate access controls create attack vectors that bypass WordPress-level security measures entirely. Server-level vulnerabilities enable 67% of successful WordPress compromises, making hosting security a critical component of comprehensive hardening strategies.
User access and authentication systems represent the human element in WordPress security architecture. Weak passwords, inadequate access controls, and social engineering attacks target user credentials to gain unauthorized system access. Brute force attacks account for 85% of all WordPress attack attempts, highlighting the importance of robust authentication hardening measures.
Database security encompasses the storage and retrieval systems managing WordPress content, user data, and configuration information. Database vulnerabilities enable data theft, content manipulation, and complete website compromise. SQL injection attacks affect 15% of WordPress installations annually, making database hardening essential for comprehensive security implementation.
Security Ninja’s architecture scanning capabilities provide comprehensive analysis across all security layers, identifying vulnerabilities and misconfigurations that manual assessments often miss. The platform’s risk scoring system prioritizes security issues based on exploitability and potential impact, enabling efficient resource allocation for maximum security improvement.
2. Core WordPress Hardening Techniques
WordPress security hardening begins with fundamental configuration changes that eliminate common vulnerabilities and strengthen core security mechanisms. These essential techniques form the foundation for advanced security implementations and provide immediate protection against the most prevalent attack vectors.
2.1 WordPress Configuration Security
The wp-config.php file contains critical security settings that control WordPress behavior and access permissions. Proper configuration of this file prevents unauthorized access, limits information disclosure, and establishes secure communication protocols.
Security Keys and Salts Implementation
define(‘AUTH_KEY’, ‘your-unique-auth-key-here’);
define(‘SECURE_AUTH_KEY’, ‘your-unique-secure-auth-key-here’);
define(‘LOGGED_IN_KEY’, ‘your-unique-logged-in-key-here’);
define(‘NONCE_KEY’, ‘your-unique-nonce-key-here’);
define(‘AUTH_SALT’, ‘your-unique-auth-salt-here’);
define(‘SECURE_AUTH_SALT’, ‘your-unique-secure-auth-salt-here’);
define(‘LOGGED_IN_SALT’, ‘your-unique-logged-in-salt-here’);
define(‘NONCE_SALT’, ‘your-unique-nonce-salt-here’);
Debug Mode and Error Reporting Configuration
define(‘WP_DEBUG’, false);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_LOG’, false);
define(‘WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY’, false);
define(‘SCRIPT_DEBUG’, false);
Database Security Configuration
$table_prefix = ‘wp_7x9k_’;
File Editing Restrictions
define(‘DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT’, true);
define(‘DISALLOW_FILE_MODS’, true);
2.2 File and Directory Permission Optimization
WordPress file permissions control access to website files and directories, preventing unauthorized modifications and data theft. Proper permission configuration follows the principle of least privilege, granting minimum access required for functionality.
Core File Permissions
WordPress core files require specific permission settings to maintain security while enabling proper functionality:
- WordPress root directory: 755 (drwxr-xr-x)
- wp-config.php: 600 (-rw——-)
- WordPress core files: 644 (-rw-r–r–)
- WordPress directories: 755 (drwxr-xr-x)
- wp-content directory: 755 (drwxr-xr-x)
- Plugin and theme files: 644 (-rw-r–r–)
- Upload directories: 755 (drwxr-xr-x)
Automated Permission Management
Security Ninja provides automated file permission scanning and correction, identifying incorrect permissions and implementing proper settings with single-click remediation. This automation ensures consistent permission management across large WordPress installations.
2.3 Database Security and Access Control
WordPress database security requires multiple hardening layers, including access control, privilege limitation, and connection security. These measures prevent unauthorized data access and protect against injection attacks.
Database User Privilege Limitation
Recommended Database Privileges:
- SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE (required)
- CREATE, DROP, ALTER (development only)
- GRANT, SUPER, PROCESS (never required)
Database Connection Security
Connection Security Measures:
- SSL/TLS encryption for database connections
- Strong database passwords (minimum 16 characters)
- Database server firewall configuration
- Connection timeout limitations
- Failed login attempt monitoring
2.4 Authentication and Authorization Hardening
WordPress authentication systems require comprehensive hardening to prevent credential-based attacks and unauthorized access. These measures strengthen user verification and access control mechanisms.
Strong Password Enforcement
Password policies should enforce complexity requirements, regular updates, and unique credentials across different systems. Weak passwords enable brute force attacks and credential stuffing attempts.
Password Requirements:
- Minimum 12 characters length
- Mixed case letters, numbers, symbols
- No dictionary words or personal information
- Unique passwords for each account
- Regular password updates (90-day cycle)
Two-Factor Authentication Implementation
Two-factor authentication adds an additional security layer beyond passwords, requiring secondary verification through mobile devices, hardware tokens, or biometric systems. This significantly reduces successful credential-based attacks.
Login Attempt Limitations
Brute force attack prevention requires limiting login attempts and implementing progressive delays for failed authentication. These measures prevent automated password guessing while maintaining usability for legitimate users.
Login Security Configuration:
- Maximum 5 failed attempts per IP address
- Progressive delay increases (1, 5, 15, 60 minutes)
- Account lockout after repeated failures
- Email notifications for security events
- IP address whitelist for administrators
3 Advanced Server & Network Hardening
Server-level security hardening extends WordPress protection beyond application-specific measures, implementing infrastructure security that prevents attacks from reaching WordPress entirely. These advanced techniques require technical expertise but provide the strongest security foundation.
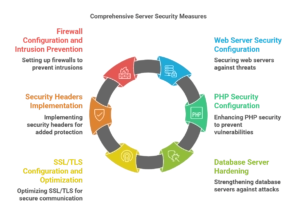
3.1 Web Server Security Configuration
Web server hardening involves configuring Apache, Nginx, or other server software to minimize attack surfaces and implement security controls at the infrastructure level.
Apache Security Hardening
# Hide server information
ServerTokens Prod
ServerSignature Off
# Disable unnecessary modules
LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
# Remove unused modules
# Security headers
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
Header always set X-Frame-Options DENY
Header always set X-XSS-Protection “1; mode=block”
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security “max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains”
# Directory access restrictions
<Directory />
Options -Indexes -Includes -ExecCGI
AllowOverride None
Require all denied
</Directory>
Nginx Security Configuration
Nginx hardening focuses on security headers, access controls, and performance optimization:
# Hide server information
server_tokens off;
# Security headers
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
add_header X-XSS-Protection “1; mode=block”;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security “max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains”;
# Rate limiting
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=login:10m rate=1r/s;
limit_req zone=login burst=5 nodelay;
# File access restrictions
location ~* \.(htaccess|htpasswd|ini|log|sh|sql|conf)$ {
deny all;
}
3.2 PHP Security Configuration
PHP Security Directives
Critical PHP security settings prevent dangerous operations and limit attack vectors:
# Disable dangerous functions
disable_functions = exec,passthru,shell_exec,system,proc_open,popen,curl_exec,curl_multi_exec,parse_ini_file,show_source
# File upload restrictions
file_uploads = On
upload_max_filesize = 10M
max_file_uploads = 5
# Execution limits
max_execution_time = 30
max_input_time = 60
memory_limit = 256M
# Error reporting
display_errors = Off
log_errors = On
error_log = /var/log/php_errors.log
# Session security
session.cookie_httponly = 1
session.cookie_secure = 1
session.use_strict_mode = 1
3.3 Database Server Hardening
Database security extends beyond WordPress-specific configurations to include server-level protections and access controls.
MySQL/MariaDB Security Configuration
Database server hardening involves multiple configuration changes and security procedures:
— Remove anonymous users
DELETE FROM mysql.user WHERE User=”;
— Remove test database
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS test;
— Secure root account
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘strong-password’) WHERE User=’root’;
— Remove remote root access
DELETE FROM mysql.user WHERE User=’root’ AND Host NOT IN (‘localhost’, ‘127.0.0.1’, ‘::1’);
— Flush privileges
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Database Configuration Security
MySQL configuration file hardening prevents unauthorized access and limits attack capabilities:
[mysqld]
# Network security
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
skip-networking = false
port = 3306
# Access controls
local-infile = 0
secure-file-priv = /var/lib/mysql-files/
# Logging
log-error = /var/log/mysql/error.log
slow-query-log = 1
slow-query-log-file = /var/log/mysql/slow.log
# SSL configuration
ssl-ca = /etc/mysql/ssl/ca-cert.pem
ssl-cert = /etc/mysql/ssl/server-cert.pem
ssl-key = /etc/mysql/ssl/server-key.pem
3.4 SSL/TLS Configuration and Optimization
Secure communication protocols protect data transmission between users and websites, preventing interception and manipulation attacks.
SSL Certificate Implementation
SSL certificates enable HTTPS encryption and provide authentication verification. Modern implementations should use strong encryption algorithms and proper certificate chains.
SSL Configuration Best Practices:
- Use certificates from trusted Certificate Authorities
- Implement HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
- Configure perfect forward secrecy
- Disable weak cipher suites and protocols
- Enable OCSP stapling for performance
- Implement certificate transparency monitoring
Apache SSL Configuration
<VirtualHost *:443>
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/certificate.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /path/to/private.key
SSLCertificateChainFile /path/to/chain.crt
# Strong SSL configuration
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1
SSLCipherSuite ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
SSLHonorCipherOrder on
# HSTS header
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security “max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload”
</VirtualHost>
3.5 Security Headers Implementation
HTTP security headers provide browser-level protection against various attack vectors, including cross-site scripting, clickjacking, and content injection.
Essential Security Headers
# Content Security Policy
Header always set Content-Security-Policy “default-src ‘self’; script-src ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’; style-src ‘self’ ‘unsafe-inline’; img-src ‘self’ data: https:; font-src ‘self’ https:; connect-src ‘self’; frame-ancestors ‘none’;”
# X-Frame-Options
Header always set X-Frame-Options “DENY”
# X-Content-Type-Options
Header always set X-Content-Type-Options “nosniff”
# X-XSS-Protection
Header always set X-XSS-Protection “1; mode=block”
# Referrer Policy
Header always set Referrer-Policy “strict-origin-when-cross-origin”
# Permissions Policy
Header always set Permissions-Policy “geolocation=(), microphone=(), camera=()”
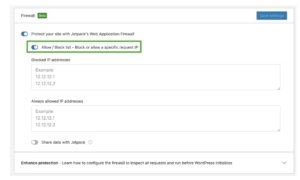
3.6 Firewall Configuration and Intrusion Prevention
Network-level security controls prevent malicious traffic from reaching WordPress applications, providing the first line of defense against attacks.
Web Application Firewall (WAF) Implementation
WAF solutions filter HTTP traffic based on predefined rules and behavioral analysis, blocking malicious requests before they reach WordPress.
WAF Protection Features:
- SQL injection prevention
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) blocking
- Brute force attack mitigation
- DDoS protection and rate limiting
- Geographic IP blocking
- Known malicious IP blacklisting
Server Firewall Configuration
Operating system firewalls control network access at the server level, limiting connections to essential services only.
# UFW firewall configuration
ufw default deny incoming
ufw default allow outgoing
ufw allow ssh
ufw allow 80/tcp
ufw allow 443/tcp
ufw enable
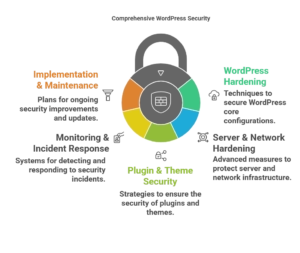
4 Plugin & Theme Security Hardening
Third-party WordPress plugins and themes introduce the highest security risks, requiring comprehensive evaluation, monitoring, and hardening procedures. These components often lack the security rigor of WordPress core development, making them primary targets for attackers.
4.1 Plugin Security Assessment and Management
Plugin security evaluation requires systematic analysis of code quality, developer reputation, update frequency, and vulnerability history. This assessment process identifies high-risk plugins and guides security-focused selection decisions.
Plugin Evaluation Criteria
Comprehensive plugin assessment considers multiple security factors:
Developer Reputation Analysis:
- WordPress.org developer profile and history
- Plugin portfolio quality and maintenance
- Security response time for reported vulnerabilities
- Community feedback and support quality
- Commercial plugin vendor security practices
Code Quality Assessment:
- WordPress coding standards compliance
- Security best practices implementation
- Input validation and output sanitization
- Database query security (prepared statements)
- File handling and upload security
Update and Maintenance Patterns:
- Regular update frequency and consistency
- WordPress version compatibility maintenance
- Security patch response time
- End-of-life planning and communication
- Backward compatibility considerations
Vulnerability History Analysis:
- Previous security vulnerabilities and severity
- Patch deployment speed and effectiveness
- Vulnerability disclosure practices
- Security researcher collaboration
- Public security audit results
4.2 Theme Security Evaluation
WordPress themes require similar security assessment procedures, with additional focus on frontend security, user input handling, and template security.
Theme Security Checklist:
Template Security:
- Proper data escaping in template files
- Secure user input handling
- File inclusion security
- Database query security
- Cross-site scripting prevention
Frontend Security:
- JavaScript security implementation
- Third-party library security
- Content Security Policy compatibility
- Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) configuration
- User-generated content handling
Customization Security:
- Theme customizer security
- Custom post type security
- Widget security implementation
- Shortcode security
- Theme option validation
4.3 Code Review and Vulnerability Scanning
Regular code review and automated vulnerability scanning identify security issues in custom code and third-party components before they can be exploited.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning
Security Ninja provides comprehensive plugin and theme vulnerability scanning, comparing installed components against known vulnerability databases and identifying potential security issues.
Scanning Capabilities:
- Real-time vulnerability database updates
- Automated daily scanning schedules
- Custom code security analysis
- Dependency vulnerability checking
- Configuration security assessment
Manual Code Review Process
Critical plugins and themes require manual security review, particularly for custom development and high-risk components.
Code Review Focus Areas:
- Input validation and sanitization
- Output escaping and encoding
- SQL injection prevention
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) prevention
- Authentication and authorization
- File handling security
- Cryptographic implementation
4.4 Update Management and Version Control
Systematic update management ensures security patches are applied promptly while maintaining website stability and functionality.
Update Strategy Implementation
Staging Environment Testing:
- Automated staging environment deployment
- Update testing procedures
- Compatibility verification
- Performance impact assessment
- Rollback procedures
Production Update Deployment:
- Scheduled maintenance windows
- Automated backup creation
- Gradual rollout procedures
- Real-time monitoring
- Emergency rollback capabilities
Version Control Integration:
- Git-based version control
- Branch-based development workflow
- Code review requirements
- Automated testing integration
- Deployment automation
4.5 Third-Party Component Security
External services and APIs introduce additional security considerations, requiring careful evaluation and monitoring.
API Security Assessment:
- Authentication mechanism security
- Data transmission encryption
- Rate limiting implementation
- Error handling security
- Privacy compliance
Third-Party Service Evaluation:
- Security certification and compliance
- Data handling practices
- Incident response procedures
- Service level agreements
- Vendor security assessments
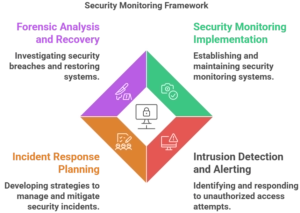
5 Monitoring & Incident Response
Continuous security monitoring and incident response capabilities enable rapid threat detection and mitigation, minimizing the impact of successful attacks and preventing escalation.
5.1 Security Monitoring Implementation
Comprehensive security monitoring requires multiple detection layers, including file integrity monitoring, log analysis, behavioral detection, and network monitoring.
File Integrity Monitoring
File integrity monitoring detects unauthorized changes to WordPress files, indicating potential compromise or malicious activity.
Monitoring Scope:
- WordPress core files
- Plugin and theme files
- Configuration files
- Upload directories
- System files and directories
Detection Capabilities:
- Real-time file change detection
- Checksum verification
- Permission change monitoring
- New file creation alerts
- Suspicious file pattern detection
Log Analysis and Correlation
Security log analysis identifies attack patterns, failed authentication attempts, and suspicious activities across multiple system components.
Log Sources:
- WordPress access logs
- Authentication logs
- Error logs
- Database logs
- System logs
- Firewall logs
Analysis Techniques:
- Pattern recognition and correlation
- Anomaly detection algorithms
- Geographic analysis
- Time-based analysis
- Behavioral profiling
5.2 Intrusion Detection and Alerting
Automated intrusion detection systems identify ongoing attacks and trigger immediate response procedures, minimizing damage and enabling rapid containment.
Behavioral Analysis
Advanced intrusion detection analyzes user behavior patterns to identify compromised accounts and insider threats.
Behavioral Indicators:
- Unusual login patterns and locations
- Abnormal file access patterns
- Suspicious database queries
- Unexpected administrative actions
- Anomalous network traffic
Real-Time Alerting
Immediate notification systems ensure security teams respond quickly to detected threats and security incidents.
Alert Categories:
- Critical security incidents
- Failed authentication attempts
- File modification alerts
- Malware detection
- Network intrusion attempts
Notification Methods:
- Email alerts with detailed information
- SMS notifications for critical incidents
- Dashboard notifications and summaries
- Integration with security information and event management (SIEM) systems
- Webhook integrations for custom workflows
5.3 Incident Response Planning
Structured incident response procedures ensure consistent and effective responses to security incidents, minimizing damage and recovery time.
Incident Classification
Security incidents require classification based on severity, impact, and required response procedures.
Severity Levels:
- Critical: Active compromise with data theft risk
- High: Confirmed malware or unauthorized access
- Medium: Suspicious activity requiring investigation
- Low: Policy violations or minor security issues
Response Procedures
Immediate Response (0-1 hours):
- Incident confirmation and classification
- Affected system isolation
- Stakeholder notification
- Evidence preservation
- Initial containment measures
Investigation Phase (1-24 hours):
- Forensic analysis and evidence collection
- Attack vector identification
- Damage assessment
- Root cause analysis
- Timeline reconstruction
Recovery Phase (24-72 hours):
- System restoration and hardening
- Security control implementation
- Monitoring enhancement
- User communication
- Business continuity restoration
Post-Incident Activities:
- Lessons learned documentation
- Process improvement implementation
- Security control updates
- Training and awareness updates
- Compliance reporting
5.4 Forensic Analysis and Recovery
Digital forensics capabilities enable detailed attack analysis and evidence collection for legal proceedings and security improvements.
Evidence Collection
Proper evidence collection ensures forensic integrity and supports legal requirements.
Collection Procedures:
- System image creation
- Log file preservation
- Network traffic capture
- Memory dump analysis
- Database backup creation
Analysis Techniques:
- Timeline analysis
- File system analysis
- Network traffic analysis
- Malware analysis
- Attribution analysis
Recovery Procedures
Systematic recovery procedures restore normal operations while implementing enhanced security controls.
Recovery Steps:
- Clean system restoration from backups
- Security control implementation
- Vulnerability remediation
- Monitoring enhancement
- User access review
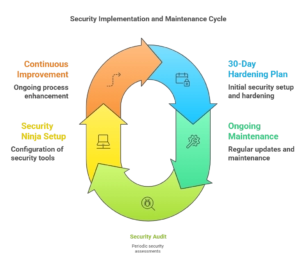
6 Implementation Roadmap & Maintenance
Successful WordPress security hardening requires systematic implementation following a structured timeline that balances security improvements with operational continuity. This roadmap provides a practical approach to achieving comprehensive security hardening within 30 days.
6.1 30-Day Hardening Implementation Plan
Week 1: Foundation Security (Days 1-7)
Day 1-2: Assessment and Planning
- Complete security audit using Security Ninja’s comprehensive scanning
- Document current security posture and vulnerabilities
- Prioritize security issues based on risk and impact
- Create implementation timeline and resource allocation
- Establish backup and recovery procedures
Day 3-4: Core WordPress Hardening
- Update WordPress core, plugins, and themes to latest versions
- Implement wp-config.php security configurations
- Generate and install new security keys and salts
- Configure file and directory permissions
- Disable file editing and unnecessary features
Day 5-6: Authentication Security
- Implement strong password policies
- Configure two-factor authentication for all users
- Set up login attempt limitations and brute force protection
- Review and update user roles and permissions
- Enable login monitoring and alerting
Day 7: Database Security
- Change database table prefixes
- Create dedicated database user with limited privileges
- Implement database connection encryption
- Configure database backup automation
- Test database recovery procedures
Week 2: Advanced Configuration (Days 8-14)
Day 8-9: Server Security Hardening
- Configure web server security headers
- Implement SSL/TLS with strong cipher suites
- Set up firewall rules and access controls
- Configure PHP security settings
- Disable unnecessary server modules and services
Day 10-11: Plugin and Theme Security
- Audit all installed plugins and themes
- Remove unused or vulnerable components
- Configure automatic security updates
- Implement plugin/theme change monitoring
- Set up vulnerability scanning schedules
Day 12-13: Network Security
- Configure Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Implement DDoS protection and rate limiting
- Set up geographic IP blocking if required
- Configure CDN security settings
- Test network security controls
Day 14: Security Monitoring Setup
- Install and configure Security Ninja monitoring
- Set up file integrity monitoring
- Configure log analysis and correlation
- Implement real-time alerting
- Test incident response procedures
Week 3: Monitoring and Testing (Days 15-21)
Day 15-16: Security Testing
- Perform penetration testing
- Conduct vulnerability assessments
- Test backup and recovery procedures
- Verify security control effectiveness
- Document testing results and improvements
Day 17-18: Monitoring Optimization
- Fine-tune monitoring thresholds
- Configure custom alerting rules
- Set up automated response procedures
- Implement security dashboards
- Train team on monitoring tools
Day 19-20: Documentation and Training
- Create security procedures documentation
- Develop incident response playbooks
- Train team members on security tools
- Establish security awareness programs
- Document configuration changes
Day 21: Final Review and Optimization
- Review all implemented security controls
- Optimize performance and usability
- Address any remaining vulnerabilities
- Finalize monitoring and alerting
- Plan ongoing maintenance procedures
Week 4: Validation and Maintenance (Days 22-30)
Day 22-24: Security Validation
- Conduct final security assessment
- Verify all hardening measures are functional
- Test incident response procedures
- Validate backup and recovery capabilities
- Confirm compliance requirements
Day 25-27: Performance Optimization
- Optimize security controls for performance
- Address any usability issues
- Fine-tune monitoring and alerting
- Implement caching and optimization
- Test website functionality
Day 28-30: Maintenance Planning
- Establish ongoing maintenance schedules
- Plan regular security assessments
- Set up automated update procedures
- Create long-term security roadmap
- Document lessons learned
6.2 Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
Daily Maintenance Tasks:
- Monitor security alerts and logs
- Review failed login attempts
- Check file integrity monitoring
- Verify backup completion
- Monitor website performance
Weekly Maintenance Tasks:
- Review security scan results
- Update plugins and themes
- Analyze security logs
- Test backup restoration
- Review user access and permissions
Monthly Maintenance Tasks:
- Conduct comprehensive security scans
- Review and update security policies
- Analyze security metrics and trends
- Update incident response procedures
- Perform security awareness training
Quarterly Maintenance Tasks:
- Conduct penetration testing
- Review and update security controls
- Assess new threats and vulnerabilities
- Update disaster recovery plans
- Evaluate security tool effectiveness
6.3 Security Audit and Assessment Schedule
Continuous Monitoring:
- Real-time threat detection and alerting
- Automated vulnerability scanning
- File integrity monitoring
- Log analysis and correlation
- Performance monitoring
Weekly Assessments:
- Security scan result review
- Vulnerability assessment updates
- Configuration compliance checking
- Access control review
- Incident analysis
Monthly Audits:
- Comprehensive security assessment
- Policy compliance review
- Risk assessment updates
- Security control effectiveness
- Business impact analysis
Annual Reviews:
- Complete security program assessment
- Threat landscape analysis
- Security strategy updates
- Compliance certification
- Security investment planning
6.4 Security Ninja Setup and Configuration
Security Ninja provides comprehensive automation for WordPress security hardening, monitoring, and maintenance. Proper setup ensures maximum security effectiveness with minimal ongoing effort.
Initial Setup Process:
Installation and Activation:
- Install Security Ninja plugin from WordPress repository
- Activate plugin and complete initial configuration
- Run comprehensive security scan
- Review scan results and prioritize issues
- Implement one-click fixes for identified problems
Advanced Configuration:
- Configure custom scanning schedules
- Set up monitoring thresholds and alerting
- Implement automated response procedures
- Integrate with external security tools
- Configure compliance reporting
Monitoring Dashboard Setup:
- Customize security dashboard layout
- Configure real-time monitoring displays
- Set up automated reporting schedules
- Implement team access controls
- Configure mobile notifications
Integration with External Tools:
- Connect with SIEM systems
- Integrate with backup solutions
- Configure CDN security settings
- Set up external monitoring services
- Implement API integrations
6.5 Continuous Improvement Process
WordPress security hardening requires ongoing improvement based on emerging threats, new vulnerabilities, and changing business requirements.
Threat Intelligence Integration:
- Monitor security advisories and vulnerability databases
- Analyze attack trends and patterns
- Update security controls based on new threats
- Implement proactive defense measures
- Share threat intelligence with security community
Security Metrics and KPIs:
- Track security incident frequency and severity
- Monitor vulnerability discovery and remediation times
- Measure security control effectiveness
- Analyze security investment ROI
- Benchmark against industry standards
Process Optimization:
- Regular review of security procedures
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- Streamlining of incident response
- Improvement of user experience
- Enhancement of team efficiency
This comprehensive WordPress security hardening guide provides the foundation for protecting your website against the evolving threat landscape of 2025. By implementing these proven techniques and leveraging Security Ninja’s advanced capabilities, you can achieve enterprise-grade security that protects your business, users, and reputation.
Remember that security hardening is an ongoing process, not a one-time implementation. Regular updates, monitoring, and improvements ensure your WordPress installation remains protected against emerging threats and maintains optimal security effectiveness throughout its operational lifetime.
Get AI-Powered Security Summary
Let AI analyze this WordPress security article and provide actionable insights from WP Security Ninja experts.